Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
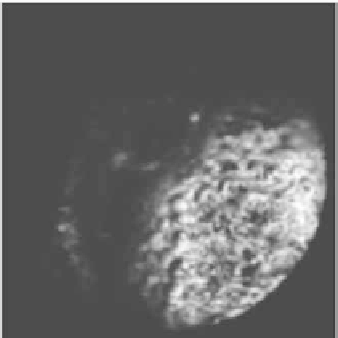
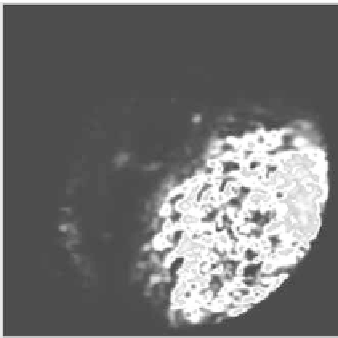
Figure 11.
Likelihood map extraction using color information: (a) original image; (b)
likelihood map for the bubbles region.
5.
STOP AND GO SNAKES DESIGN
5.1. Term Decoupling
The hypothesis we consider in the creation of our formulation is that we can
obtain a characteristic function of the region of interest. However, this does not
happen in practical applications. At this point, alternate schemes must be used as
approximations of the characteristic function to perform the decoupling needed for
the STOP and GOmodels. The only requirement for this approximation is that the
region of interest be defined as a local extremumwhile having small values outside
this area. At this point the use of the filter spaces, likelihood maps, and confidence
rate maps come into play. Recall that all these techniques comply with the above
requirement and therefore can be used as estimations of the characteristic function.
Let
L
be the estimate of the characteristic function normalized between 0
and 1. Therefore, replacing
I
by
L
in the
Stop and Go
equation, we obtain the
following:
∂
∂t
=
ακ L
n
+
ˇ
L<
n
+
V
0
(1
−
L
)
·
·
∇
·
g,n>
n.
At this point, it only remains to define the STOP term,
L
·∇
g
, which defines the
object of interest.