Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
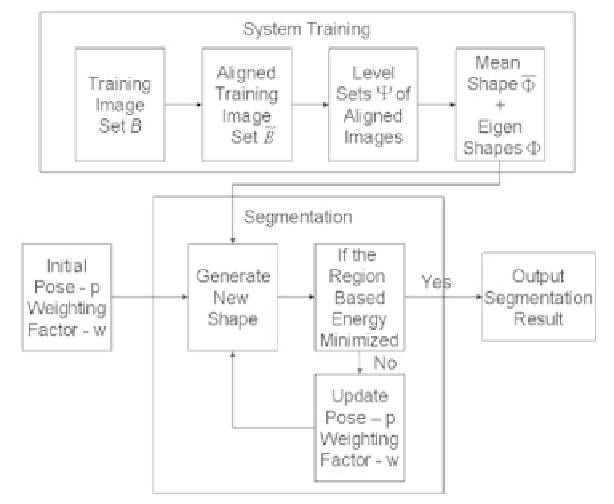
Figure 16.
Flowchart of the algorithm presented in [37]. Basically, there are two stages.
The first stage is system training to extract shape model, and the second is to segment the
image using the shape model.
E
j
align
for each binary image corresponding to the fixed one, say the first binary
image
B
1
, and the energy is defined as follows:
Ω
(
B
j
−
B
1
)
2
dA
E
j
align
=
Ω
(
B
j
+
B
1
)
2
dA
,
(31)
where Ω denotes the image domain, and
B
j
denotes the transformed image of
B
j
based on the pose parameters
p
. Minimizing this energy is equivalent tominimizing
the difference between the current binary image and the fixed image in the training
database. The normalization term in the denominator is employed to prevent the
images from shrinking to improve the cost function. Hill climbing or the Rprop
method could be applied for the gradient descent.
An example is depicted in Figures 17 and 18 regarding the alignment proce-
dure. There are in total 15 binary images about different plane shapes.
The popular and natural approach to represent shapes is by employing point
models where a set of marker points is often used to describe the boundaries of the
shape. This approach suffers fromproblems such as numerical instability, inability