Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
et introduce a unique variable
V
describing the
excitation
of the neighborhood (it
should encode all possibilities for the collective states of the neighborhood), and
note than in the case of our semitotalistic cell it is described by
5
. In
what follows we will also call
V
a
projection
because it represents a projection
from the
n-
dimensional input space to a one-dimensional (scalar) space while pre-
serving all information contained in the
n-
dimensional vector defining the collec-
tive state of the neighborhood. In general, for any semitotalistic cell with
n
inputs
the following formula stands:
V
E
D
VE D
,
(3.)
where
are defined as above, and
b
(called an
orientation
[2]) is an integer
D,
E
^
n
b
but one can optimie its value (minimie
b
) such that
for the same number
n
of inputs the gene will become smaller than
n+1
(needs
less bits). A discussion on the significance of
. Implicitly
b
0
,..
n
b
follows later within this section.
Now Table 3.1 can be rewritten as Table 3.2. ere we used the convention
w=-1
to denote an output equal to logic “0”, and we also specified the transition points,
i.e. those values of
V
such that the
w
function switches from -1 to 1 or vice-
versa. Note that any nonlinear function with the same roots as the transition points
can be selected as a nonlinear representation of the cell. In particular the simplest
solution is a polynomial function, i.e.
ws t
t
...
t
.
(3.)
V
V
V
1
2
m
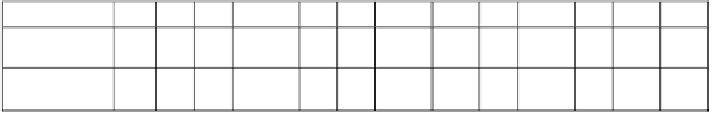
Table 3.2.
A cell definition based on the function
al dependence between the projection
V
and the output
y
(ere exemplified for ID103)
G= y(
V
)
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
w
-1
-1
-1
0
1
1
0
-1
-1
0
1
1
1
9
8
7
t
3
6
5
6
5
t
2
4
.
5
4
3
t
1
2
.
5
2
1
0
V
5
E
D
Note than any scalar function which passes through the transition points marked within the
table can implement the table.
The output value is defined by
y
sgn
w
1 /2.
(3.6)
In () the
s
(sign) variable is computed as:
sg
2 ,
(3.7)
i.e.
s
for odd ID.
Note than in the above are possible at most
for even ID and
s
1
1
transition points where
N
m
N
1
is the number of bits defining the gene
G.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search