Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2.3 Reaction-Diffusion Cellular Nonlinear Networks
eaction-diffusion CNNs (D-CNNs) [] were proposed as a particular case of
continuous-time autonomous
1
CNN and are discrete-space models of partial dif-
ferential equations describing the reaction-diffusion physical processes.
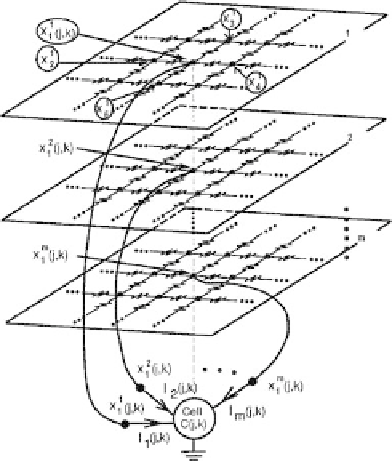
From a circuit perspective a D-CNN can be modeled as a collection of multi-
port nonlinear cells. These cells are coupled with their neighboring cells via linear
resistive networks (Fig. 3.2).
Fig. 3.2.
The topology of a reaction diffusion cellular neural network. A cell is a
m
-port de-
scribed by a nonlinear ODE which models a physical
reaction.
The coupling with neighboring
ing cells is done via resistive grids modeling the physical process of
diffusion
Example :
The case of a reactiondiffusion cell with von Neumann neighbor-
hood
. The cell equation is of the following form:
1
1
1
m
2
3
4
5
1
,
&
x
f
(
x
,
x
,...,
x
,
G
)
D
x
x
x
x
4
x
1
1
1
1
..
j
j
j
j
j
j
1
1
m
,
&
x
f
(
x
,
x
2
,...,
x
,
G
)
D
x
x
x
x
4
x
1
j
j
5
1
2
3
4
1
..
m
12
m
mmmm
m
x
&
f
(
xx x
,
,...,
,
G
)
Dxxxx x
4
,
1
m
1
1
1
m
m
2
3
4
5
1
1
n autonomous system has no external inputs. Information processing in such systems
consists in prescribing the initial state of all cells with some pattern to be processed
followed by a dynamic transformation of this pattern until a stopping criterion is met.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search