Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
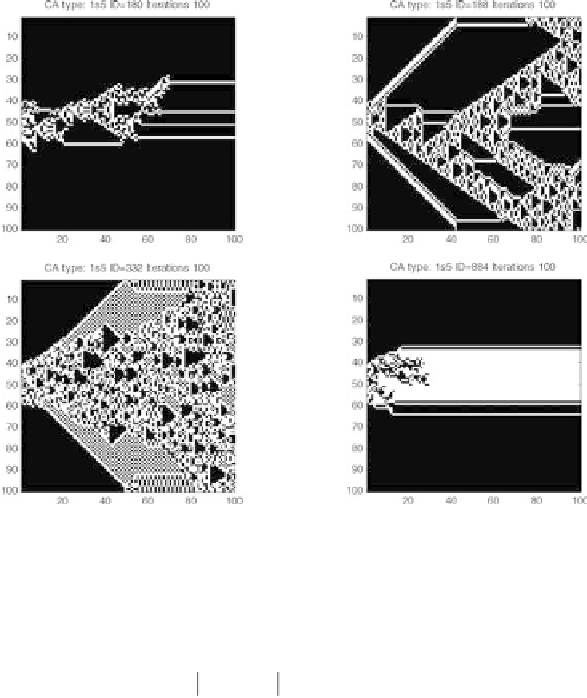
Fig. 7.7.
Several examples of complex behavior including the emergence of gliders pre-
dicted by the theory of probabilistic growth. In all cases
ID
k
8
4
In the case of a two-dimensional topology “2s5” a similar condition will in-
clude only the two least significant bits of the gene as follows:
(7.29)
yy
11.
0
1
It holds only when the two last significant bits have different values. When it
holds it gives only one possible value
ue
. Observe the lack of small
ue
values,
associated with emergence of gliders. This explains why gliders were actually not
observed within the 2s5 family. In fact the only complexity in this case is ob-
served for IDs in “case2” where quiescent states alternates and therefore an addi-
tional value of
1
ue
is possible (see (7.20)). If the 2s9 family is considered
instead, a condition of the same kind will include more bits from the ID making
thus possible more levels of
ue
and therefore low positive values associated with
interesting emergent phenomena. Experimental results actually confirmed that
many CAs from the 2s9 family exhibit interesting emergent properties, one of the
most known example being ID = 6,152 (“Game of Life”).
0
Search WWH ::

Custom Search