Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
initial state, a finite running time and a relatively small number of cells in the
simulation process.
Is it thus possible that for some IDs (like the two mentioned above) the resulting
vector of emergence measures is an exception rather than the average case. Note
however that such exceptions are usually less than the majority of genes filtered-out
by a sieving process and they have to be accepted as an uncertainty price paid for
the speed of locating interesting behaviors using the sieves. Such errors decrease if
measures of emergence are evaluated by averaging over a large numbers of different
initial states.
Such uncertainties are actually common to real life problems as they were
revealed in mathematics [86] and physics [87].
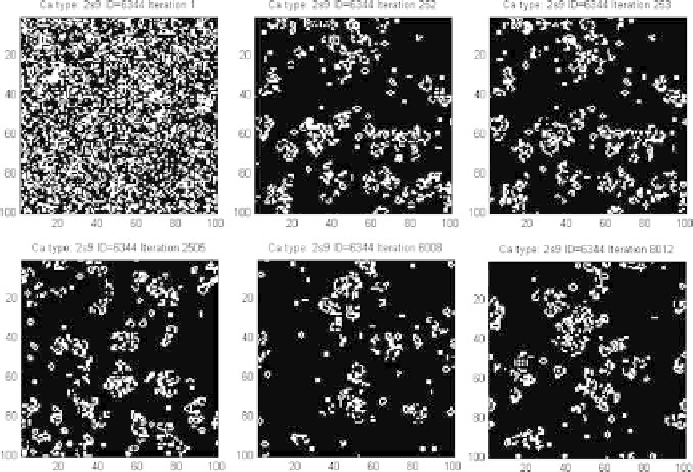
Fig. 6.3.
Snapshots of the dynamic evolution of CA with ID = 6344 exhibiting the “Eternal
- Life” property
6.3.2 Classic “Life”: Using Sieves to Locate Similar Behaviors
Let now consider the well known “Game of Life” cellular automata. Its associated cell
belong to the “2s9” family and has ID = 6152. The emergence measure vector
x
. Note the
“implosive” value of 0.03 for
U
suggesting the convergence of complex behaviors
towards a low-periodic global state. Of course, this prediction on the possible
behavior should be considered with a degree o uncertainty, as discussed above,
in this case is:
x
U,
Var,
Tr,
Clus
[
0.0331
0.0010
0.5500
0.9750]
Search WWH ::

Custom Search