Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
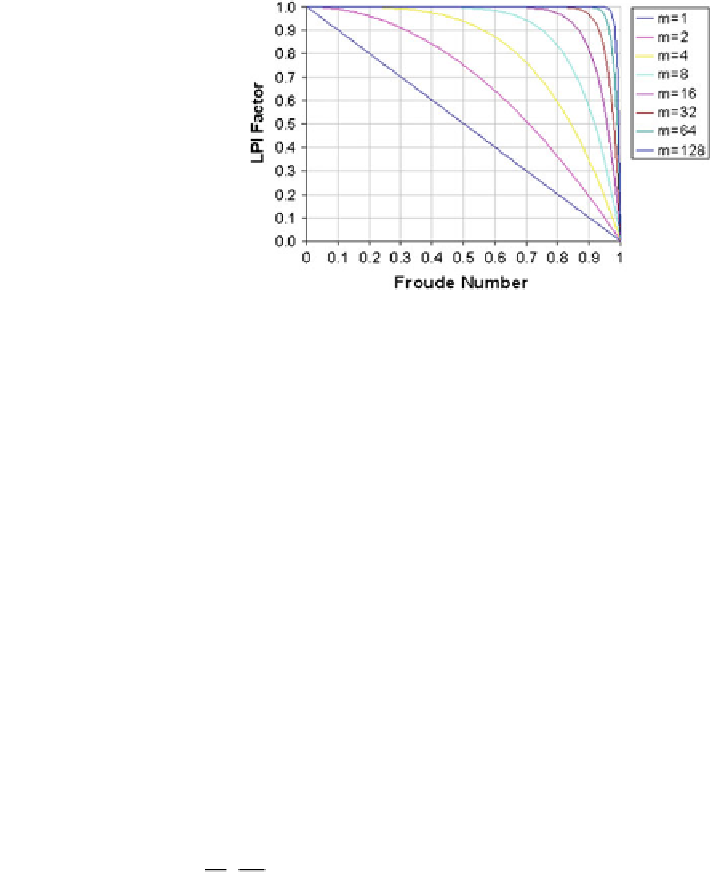
Fig. 3.9 Froude number
(Fr) = 1 represents critical
flow (HEC-RAS manual)
Ubaye River is composed of both natural and man-made channels (the upstream
is channelized, the middle and downstream parts are natural), therefore, a critical
flow scenario was considered for modeling.
3.9.4 SOBEK: Calculation Procedures
Within the 1D-2D modeling approach, a mathematical model consists of a 1D-2D
flow model [
65
] such as the SOBEK model developed by Delft Hydraulics in the
Netherlands. In this model, unsteady flow discharge varies as a function of time
and therefore, all the hydraulic factors of a cross section change, such as velocity
varying and depth of water as a function of time [
3
]. SOBEK is a model that solves
the De Saint-Venant flow equation in 1D as long as water stays within its banks.
However, when dyke/levees are breached or overtopped the model automatically
switches to 2D [
66
]; SOBEK User's manual [
67
],
www.sobek.nl
)
.
The equation is presented as follows:
o
A
t
ot
þ
o
Q
ox
¼
q
lat
ð
3
:
25
Þ
þ
gA
f
o
A
Q
2
A
f
o
Q
ot
þ
o
ox
þ
gQ
jj
W
f
s
wi
p
w
¼
0
ð
3
:
26
Þ
ox
C
2
RA
f
where:
A
f
is the wetted area (m
2
); q
lat
is the lateral discharge per unit length (m
2
/s); Q is
the discharge (m
2
/s); t is time (s); x is the distance (m); g is the gravity acceleration
(m
2
/s) = 9.81; h is the water level (m); C is the Chezy coefficient (m
1/2
/s); R is the
hydraulic radius (m); W
f
is the flow width (m); T
wi
is the wind shear stress (n/m
2
);
P
w
is the water density (kg/m
2
) = normally 1,000.
Forces caused by bed friction and earth gravity usually primarily determine
flow conditions and other forces are less important. During computation, the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search