Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
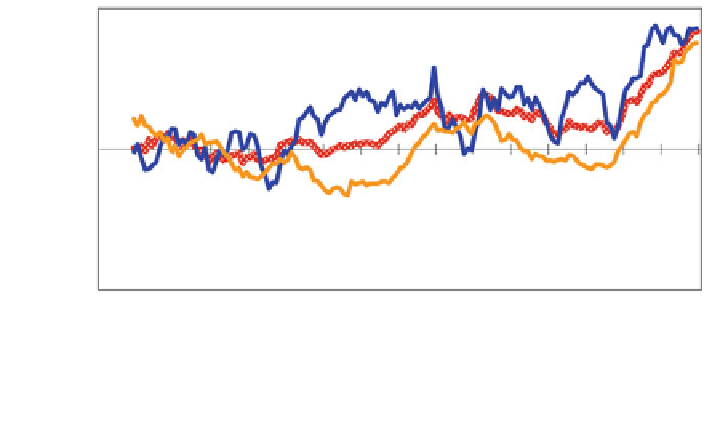
Fig. 2.5 Annual, winter (December, January, February) and summer (June, July, August) mean
temperature deviations in Europe, 1860-2009 (C). The lines refer to 10 year moving average
European land; (Source EEA's ''global and European temperature'' core set indicator, based on
gridded data from CRUTEM3, climatic research unit and KNMI's climate explorer)
Fig. 2.6 Observed temperature change over Europe 1976-2006; (Source EEA's ''Global and
European temperature'' core set indicator, based on gridded data from CRUTEM3, Climatic
Research Unit and KNMI's climate explorer)
triggering factors for floods event. The trend analysis of hydrological and mete-
orological series is important, even more relevant when considering the regional
effects of global climate change [
22
,
77
]. As the atmosphere's water holding
capacity increases with temperature, the intensified potential for extreme precip-
itation events augments the risk of inundations caused by sustained rainfall over
most land areas [
39
,
78
], especially in areas where flooding is typically triggered









































Search WWH ::

Custom Search