Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
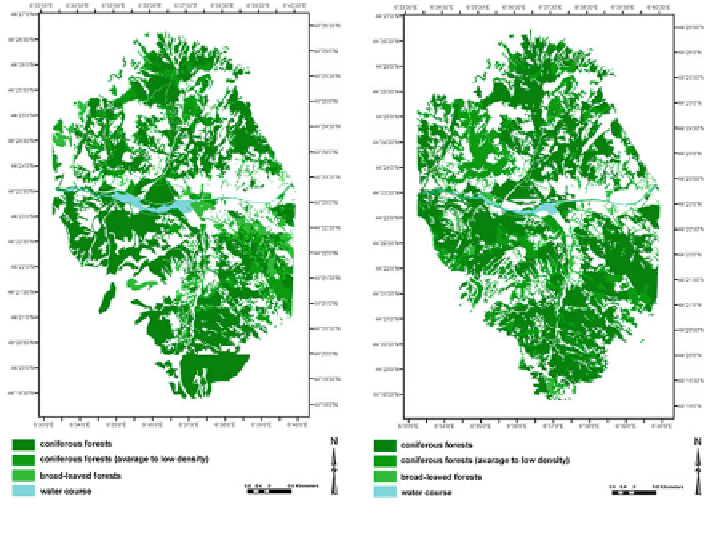
Fig. 6.86
Comparing coniferous forest in 1956 and 2004
6.14 Chapter Summary
In hydraulic modeling, the output is affected to a large extent by model input
parameters. For input data preparation, the quality of the DEM was at first con-
trolled using interpolation methods as important input data to accomplish suc-
cessful modeling. The results showed that the quality of the original DEM was
sufficient enough for modeling. The hydrological tool in ArcGIS was applied only
to fill the probable sinks in DEM. In the next step, the original DEM was con-
sidered as the reference data source, and then different interpolation techniques
were compared to access the best method to interpolate DEM based on observed
data points. For this purpose, different statistical analysis methods including Q-Q
plot and spatial analysis were applied to estimate the errors.
Before starting hydrodynamic modeling, based on the available data, land use
maps from 1956 to 2004 were analyzed to gain better insight on river morphology
changes over time and to access a variety of roughness derived from different land
use maps to assign the cross sections in the flood modeling phase. Then, the focus
was on preparing hazard maps and frequency analysis. The main purpose here was
to compare some severe flood events that occurred in this area and to estimate
flood propagation using hydrodynamic models (One dimensional (1D) HEC-RAS
model and one-two dimensional (1D-2D) SOBEK model), with respect to a
variety of cross sections, river morphology and different hydrographs. Moreover,
the preparation of different hydrological scenarios for civil protection purposes
Search WWH ::

Custom Search