Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Overtopping
Overtopping
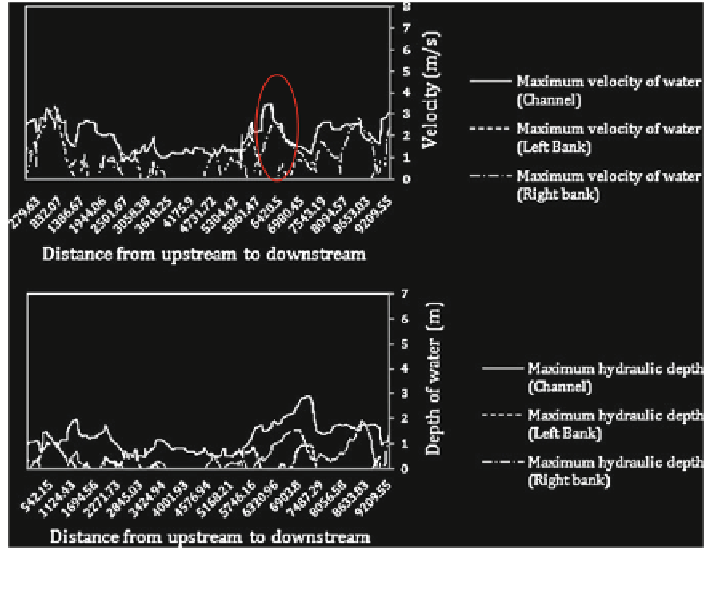
Fig. 6.42 Scenario (1); estimated velocity (m/s) and depth of water (m), food 2008; (modeling
with considering the dyke)
In this simulation which was based on flood 2008, if no major flooding
occurred, some damages were observed: a bridge had been destroyed, and in some
specific areas, river ridges have been scored.
Scenario (2): Modeling of the 2008 flood event showed a maximum discharge
of 205 m
3
/s without the dykes. Scenario (2) is affected by the channel maintenance
and structural dyke integrity. The assumption was that the lack of maintenance
produced the dyke break. The results showed that the banks were overtopped by
the flood (Figs.
6.43
and
6.44
).
By comparing this scenario with previous one, it could be concluded that in
case of dyke failure, the capacity of the channel is not enough to keep the water
between the banks and in several locations strong overtopping leads to inundation
in the floodplain in both sides of the Ubaye River in both city and environmental
parts. The velocity and depth of water along the river and across the floodplain is
not as stronger as flood 1957 due to lower amount of discharge applied in this
scenario.
Figure
6.45
represents sample cross sections located just before and after the
dyke break.
Supporting scenario (3): Modeling of the 1957 flood event with a maximum
discharge of 480 m
3
/s, considering the dyke. This scenario was used as support
scenario only for comparing with other scenarios (Fig.
6.46
).



Search WWH ::

Custom Search