Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
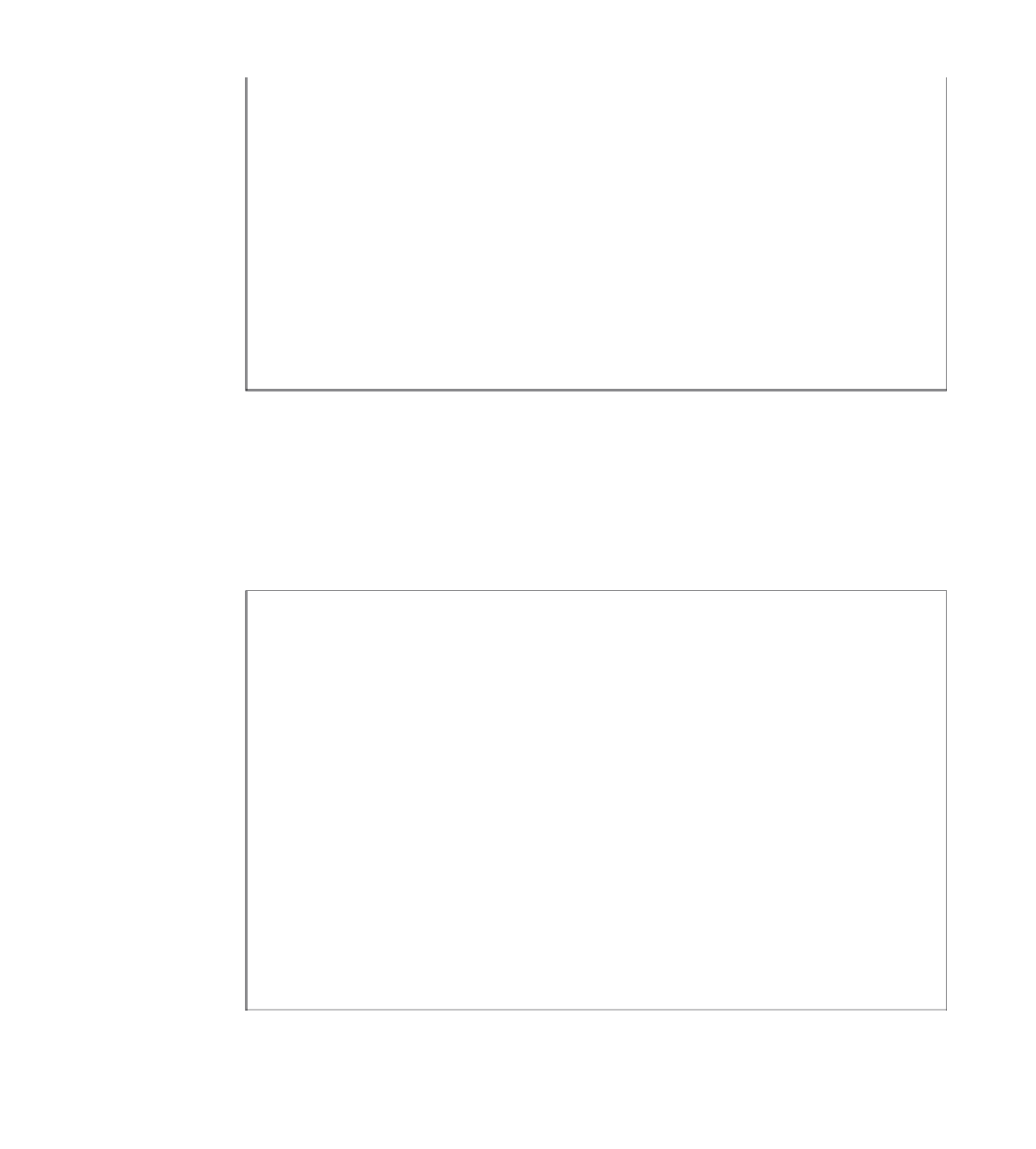
Example 12-5
show bgp ipv6 summary
Output (Continued)
2 BGP path attribute entries using 120 bytes of memory
4 BGP rrinfo entries using 96 bytes of memory
1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP activity 15/22 prefixes, 32/21 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2001:400:0:701::701
4 65001 29 33 5 0 0 00:06:26 1
2001:400:0:1234::2
4 65000 53 54 5 0 0 00:05:39 2
2001:400:0:1234::3
4 65000 53 53 5 0 0 00:05:48 2
2001:400:0:1234::6
4 65000 52 63 5 0 0 00:05:14 1
The output from
show bgp ipv6 summary
lists the BGP peers and their current state. If the
peers are in a state other than Established, that state is identified. In Example 12-5, all
the peers are in an Established state.
IPv6 prefix information carried in BGP is shown with the
show bgp ipv6
command, as
shown in Example 12-6.
Example 12-6
IPv6 BGP Table Display
R5#show bgp ipv6
BGP table version is 19, local router ID is 10.5.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i2001:400::/29 2001:400:0:1234::4
0 100 0 i
* i 2001:400:0:1234::4
0 100 0 i
* i2001:400:0:1234::7/128
2001:400:0:701::701
0 100 0 65001 i
*>i 2001:400:0:701::701
0 100 0 65001 i
*> 2001:500::/29 :: 0 32768 i
* i2001:600::/29 2001:400:0:1234::6
0 100 0 i
*>i 2001:400:0:1234::6
0 100 0 i