Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Source Tree
A source tree, or SPT, is defined by an (S,G) entry in the multicast route table. This tree is
specific to a single source, and only multicast packets from this source are forwarded down
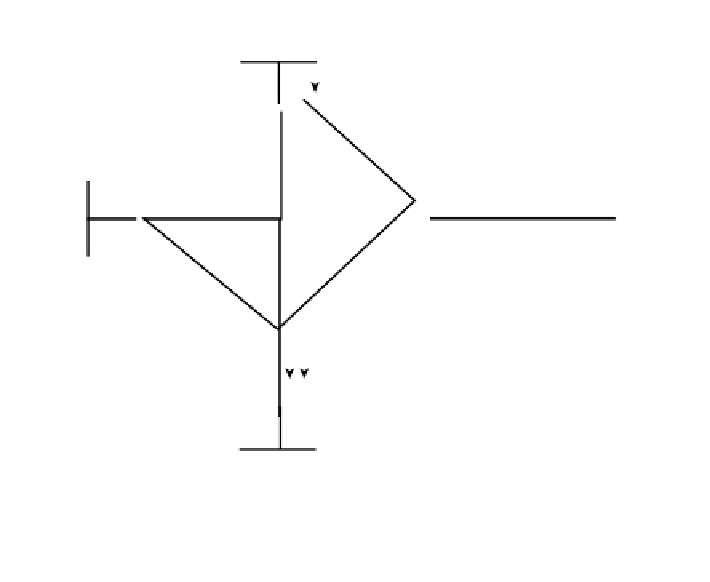
the source tree. Figure 11-5 shows an example of multiple sources each using their own SPT.
Figure 11-5
Source Tree Distribution Tree
Receiver
Source
Receiver
In Figure 11-5, each source has its own distribution tree. Even if some portions overlap,
there are separate trees with separate forwarding information. These forwarding trees are
not combined. Traffic arrives at the router on the interface that faces back toward the source.
Traffic is sent out the interfaces in the MDT other than the interface on which it arrived. If
an (S,G) does not exist, the (*,G) entry is used.
Building Multicast Distribution Trees
The primary protocol for building MDTs is Protocol-Independent Multicast (PIM). Unlike
its predecessor, Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP), PIM relies on the
unicast routing protocol to provide topological information. This chapter does not discuss
DVMRP, because PIM is the recommended protocol for deploying IP multicast.