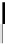Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
When PE2 finally receives PE1's loopback address, there are two labels:
•
One IGP label to reach ASBR4 via RR2 (L9), label value 17
•
One BGP label to reach PE1 via ASBR4 (L8), label value 20
For the VPN prefix 172.16.0.0/16, there is also a third label, Lv, with a label value of 22.
Example 10-33 shows the label stack on PE2, where 192.168.47.7 is RR2.
Example 10-33
Label Stack on PE2
PE2#show ip cef vrf VPNa 172.16.0.0
172.16.0.0/16, version 6, epoch 0, cached adjacency 192.168.47.7
0 packets, 0 bytes
tag information set
local tag: VPN-route-head
fast tag rewrite with Et1/0, 192.168.47.7, tags imposed: {17 20 22}
via 192.168.100.2, 0 dependencies, recursive
next hop 192.168.47.7, Ethernet1/0 via 192.168.100.2/32
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with Et1/0, 192.168.47.7, tags imposed: {17 20 22}
Figure 10-25 shows packet forwarding with a non-VPN transit AS. To reach 172.16.0.0/16
from VPNa, PE2 performs a recursive lookup of the BGP next hop PE1 and resolves to a
BGP next hop of ASBR4. One more lookup resolves to an IGP next hop of RR2. When PE2
receives a packet to 172.16.0.0/16 from VPNa, three labels are imposed:
•
The top label (17) to reach ASBR4 via RR2
•
The middle label (20) to reach PE1 via ASBR4
•
The bottom label (22) to reach 172.16.0.0/16 in VPNa
Figure 10-25
Packet Forwarding with a Non-VPN Transit AS
RR1
RR2
20
22
IP Packet
17
22
IP Packet
18
22
IP Packet
19
22
IP Packet
PE2
PE1
ASBR1
ASBR2
ASBR3
ASBR4
AS 100
AS 200
AS 300
22
IP Packet
19
22
IP Packet
17
20
22
IP Packet