Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
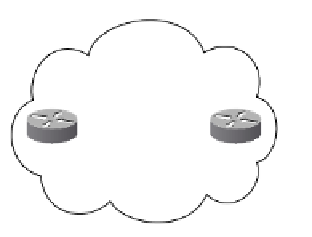
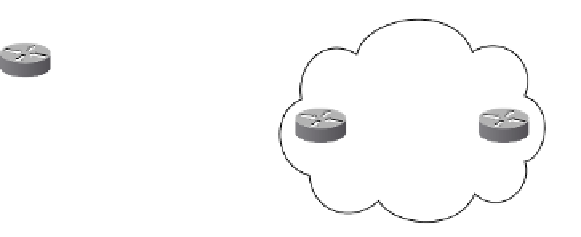
on ASBRs. Figure 10-20 shows such a scenario. In each AS, a PE peers only with the RR
in its own AS to exchange VPNv4 prefixes via multiprotocol iBGP. Two RRs exchange
VPNv4 information via multihop multiprotocol eBGP. Two ASBRs exchange only IPv4
information, not VPNv4 information.
Figure 10-20
Multihop Multiprotocol eBGP Using RRs
Multi-hop eBGP
for VPNv4
RR1
RR2
Single-hop
eBGP for
IPv4 with Labels
PE1
ASBR2
ASBR1
PE2
AS 200
AS 100
As seen previously in this chapter, any BGP next-hop change resets the label stack. To
create an end-to-end LSP between two PE devices, the BGP next hop of the remote PE must
not be changed when crossing AS borders. If the BGP next hop is reset on RRs, new label
stacks have to be created. The solution to this problem is to force RRs to advertise VPNv4
prefixes without resetting the next hop. You do this by configuring
neighbor next-hop-
unchanged
between the two RRs.
For both RRs to establish a BGP session, there must be IPv4 reachability between them.
Within its respective AS, there is already an IGP LSP between a PE and an ASBR and
between an RR and an ASBR. You need to connect the LSPs between the two autonomous
systems.
Because eBGP for IPv4 is already running between the two autonomous systems, one
obvious solution is to use BGP to carry labels for IPv4 prefixes. As indicated in Chapter 2,
carrying labels for IPv4 prefixes is an option provided by the BGP multiprotocol capability.
To send labels, use the BGP command
neighbor send-label
under the IPv4 address family.
To have an end-to-end LSP carry VPN traffic, the loopback addresses of the remote RRs
and PEs must be reachable with proper labels by the local RRs and PEs. There are two ways
to make this happen:
•
ASBRs redistribute the loopback addresses of RRs and PEs that are in eBGP into the
IGP in the local AS. This method is simple to accomplish but might be inappropriate
if the addresses to be distributed are large and unstable. Proper filtering is required.
•
ASBRs advertise the loopback addresses of remote RRs and PEs in IPv4 iBGP with
labels to local RRs and PEs. This method isolates the local IGP from addresses in
another AS. Because more labels are involved, this method is more complex to support.