Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The path from the ingress LER R2 to the egress LER R5 or the reverse is called a
Label
Switched Path (LSP)
. Labels have local significance and are typically exchanged using a
signaling protocol.
An IP packet is classified only once when entering the MPLS network. Thereafter, the
original IP packet is encapsulated into a labeled packet and is switched based on the labels,
not its IPv4 header. On the egress LER, the labeled packet is decapsulated into an IP packet
and is delivered using conventional IP forwarding.
Rather than thinking of MPLS as a network service, MPLS is often considered more appro-
priately an enabling technology. MPLS provides a connection-oriented infrastructure that
lets other service-oriented technologies be deployed. MPLS VPN is one such example.
Additionally, traffic engineering (TE), quality of service (QoS), and Layer 2 simulation can
be provisioned over MPLS.
The next sections provide an overview of the types of MPLS labels, how labels are
exchanged between LSR pairs, and how labeled packets are processed.
MPLS Labels
MPLS labels can take a variety of forms, depending on the underlying links. With regards
to label implementation, there are three general types of networks:
•
Frame-based
•
Cell-based
•
Non-packet-based
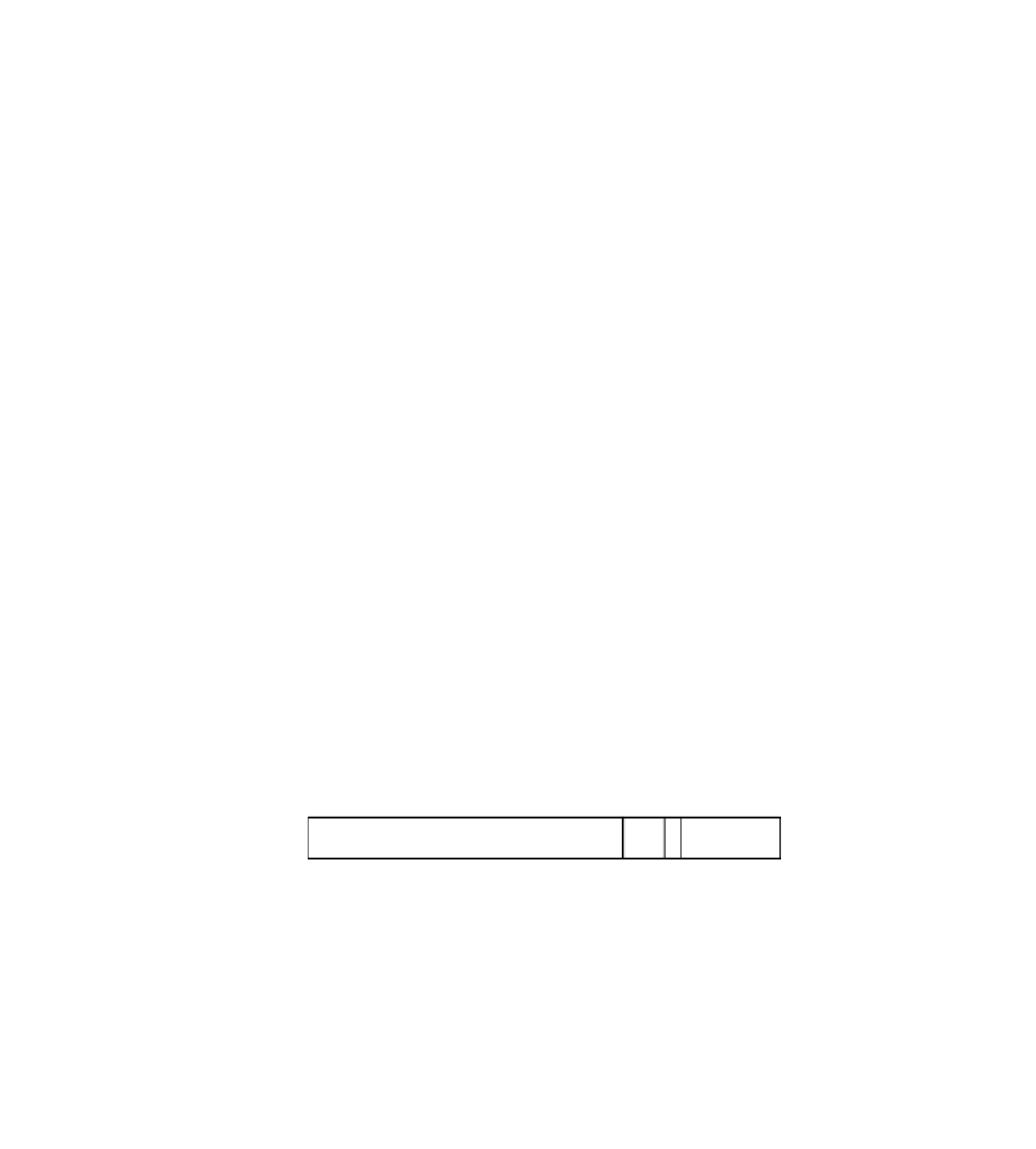
Figure 10-2 shows the format of a label in a frame-based network such as Ethernet. The
label value is a 20-bit field that carries the label's actual value. When a labeled packet is
received, the label value at the top of the stack is looked up (a stack is a concatenation of
one or more labels). From the lookup, the packet's next hop is learned, and the type of
operation to be performed can be determined on the label stack before forwarding.
Figure 10-2
Frame Label Header Format
Label Value
Exp
S
TTL
20 Bits
3 Bits
1 Bit
8 Bits
The following describes each of the fields in the frame-based label header:
•
Exp field
—The 3-bit Experimental Bits (Exp) field is typically used to convey the
packet's class of service, as the Precedence bits do in the IPv4 header.