Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
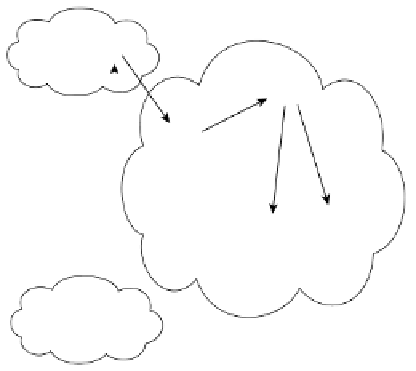
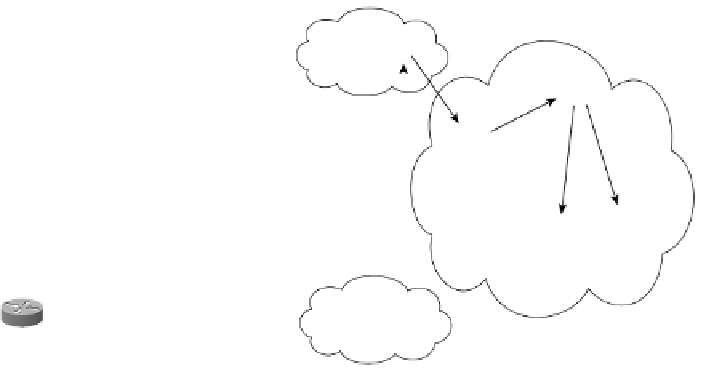
Figure 7-32
Peer Groups with RR for IOS 12.0 or Later
AS 200
AS 200
AS 100
AS 100
R6
R6
RR
RR
R3
R3
R1
R1
Update 172.16.0.0/16
Client
Client
X
R5
R5
R2
R2
R4
R4
172.16.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/16
Client
Client
Client
Client
AS 300
AS 300
172.16.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/16
R7
R7
Prefix Propagation
RR's Best Path via R2
Confederation
As indicated in the previous section, route reflection solves the iBGP scalability issue by
relaxing the iBGP advertisement rule for RRs. These routers can reflect routes between
clients they serve and other iBGP peers; thus, clients need to peer only with RRs. Confed-
eration approaches the same issue from a different angle. This section discusses various
aspects of confederation and its design guidelines.
How Confederation Works
Confederation solves the full iBGP mesh issue by splitting a large AS into a number of
smaller autonomous systems, called
member autonomous systems
or
subautonomous
systems
. Because eBGP sessions are used among member autonomous systems, no full
mesh is required. Within each member AS, however, the iBGP full-mesh requirement still
applies.
The eBGP session within a confederation is slightly different from a regular eBGP session.
To differentiate between the two, this type of eBGP session is called an
intraconfederation
eBGP session
. When the session is initially brought up, it behaves exactly like an eBGP
session. In other words, no verification is made on both peers to determine if the session is
a true eBGP or confederation eBGP session. The difference comes in when propagating