Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The next option is to receive partial routing information. The enterprise can request that the
upstream providers send only their locally originated prefixes and those prefixes for their
customers. This lets the enterprise correctly route traffic destined for either provider. A
default route directed at each provider is still required to reach any destinations that are
beyond the immediate upstream providers and their customers.
The enterprise can also receive full tables from both providers. This allows the enterprise
border router to send traffic to the upstream provider that is logically closest to the desti-
nation. This logical distance is derived from the AS_PATH. If the AS_PATH is the same
length, the traffic is sent to the upstream provider whose path has the lowest ROUTER_ID.
Multiple Border Routers
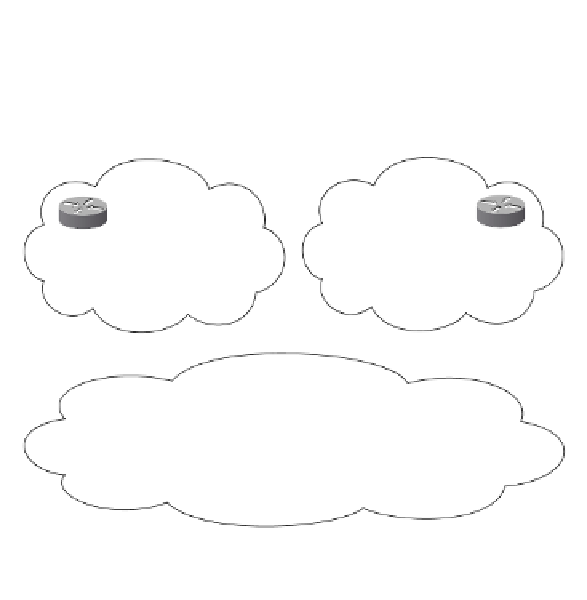
The standard multihomed network with multiple border routers design, shown in Figure 6-5,
is the most common for medium and large businesses. The highest level of redundancy is
provided through multiple providers, multiple circuits, and multiple enterprise border
routers.
Figure 6-5
Multihomed Multiple Border Router Architecture
Internet
Provider B (AS 200)
Provider A (AS 100)
Enterprise (AS 300)