Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
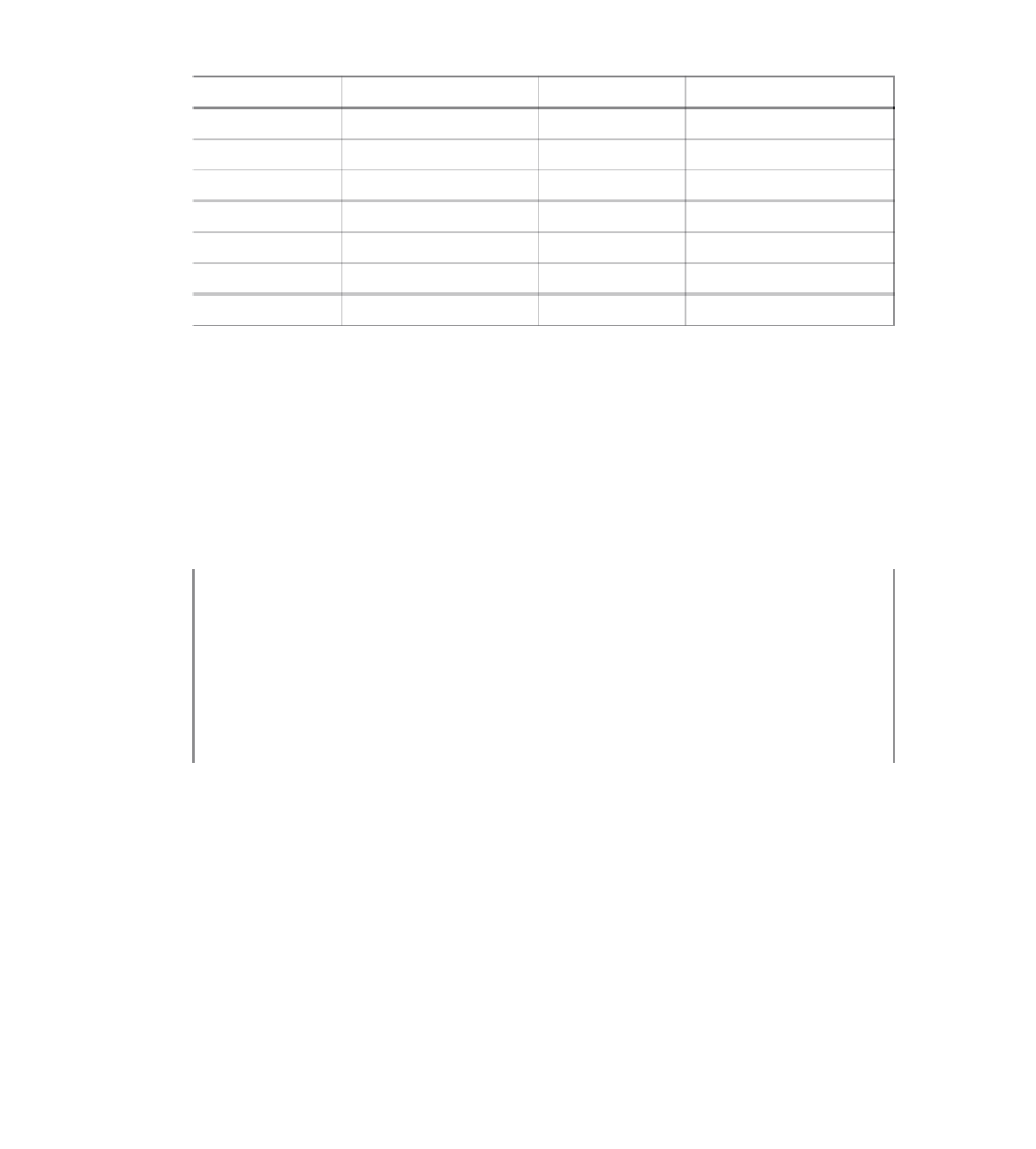
Table 5-3
Loopback Address Assignments
Router Name
Loopback Address
Router Name
Loopback Address
R1
172.16.1.1/24
R8
172.16.8.1/24
R2
172.16.2.1/24
R9
172.16.9.1/24
R3
172.16.3.1/24
R10
172.16.10.1/24
R4
172.16.4.1/24
R11
172.16.11.1/24
R5
172.16.5.1/24
R12
172.16.12.1/24
R6
172.16.6.1/24
R13
172.16.13.1/24
R7
172.16.7.1/24
—
—
It is not necessary to use a /24 for each loopback. In fact, it is considered a good practice
to use a /32. However, it is common for /24s to be used for loopback interfaces in the
enterprise environment. /24s are used in this example for clarity.
NOTE
Example 5-23 shows the configuration template that should be used on each router.
Example 5-23
Configuration Template for the Supporting Infrastructure
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.X.0 255.255.255.0
!
router eigrp 100
no auto-summary
network 10.0.0.0
network 172.16.0.0
!
The new Internet routers should also be installed during this stage to provide origination
of the default route when BGP is configured. The Internet routers do not need to join the
EIGRP AS. They only need to be connected to what will be the DMZ Ethernet segment in
each location with Internet connectivity. At this point, the proxy-based Internet connectivity
is still being used.
Overlay BGP and Inject Prefixes
The next part of the migration involves deploying the BGP configuration and injecting the
prefixes from EIGRP into BGP. The administrative distance for BGP is configured to be