Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
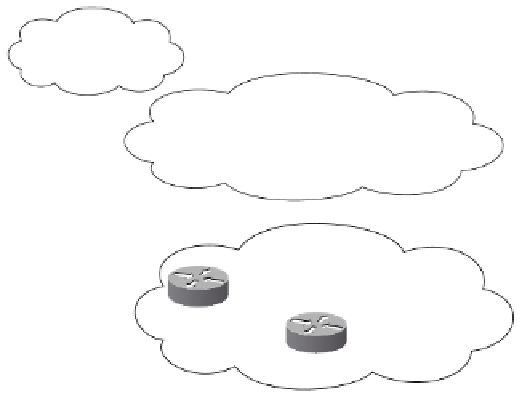
Figure 4-4
Example of Conditional Injection
AS 300
AS 400
192.168.46.0/24
192.168.57.0/24
R6
R7
AS 200
172.16.1.0/24
172.16.2.0/24
192.168.45.0/24
R4
R5
172.16.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.24.0/24
192.168.35.0/24
AS 100
192.168.23.0/24
R3
R2
192.168.13.0/24
192.168.12.0/24
R1
With traffic statistics analysis, AS 100 determines that the best exit for 172.16.1.0/24 is via
R2. It is also found that the best exit to 172.16.2.0/24 is via R3. In an effort to optimize the
exit points, conditional injection is deployed on R2 and R3. The network address for each
link is specified in Figure 4-4, with each router's number as the host address.
Example 4-24 shows a sample BGP configuration on R2. The route map
AS200-aggregate
matches the incoming aggregate from R4. If the match is positive, create 172.16.1.0/24 in
the local BGP RIB. To prevent the injected routes from leaking back out, a community of
no-export
is set for the injected route. Also, a community of 100:200 is tagged for the route
to indicate that it is a locally injected specific from AS 200.
Example 4-24
Sample BGP Configuration on R2
router bgp 100
bgp inject-map AS200-specific exist-map AS200-aggregate
neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 192.168.12.1 send-community
neighbor 192.168.23.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 192.168.23.3 send-community
neighbor 192.168.24.4 remote-as 200
!
ip bgp-community new-format
ip prefix-list AS200-R4 seq 5 permit 192.168.24.4/32
ip prefix-list Aggregate seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/16
ip prefix-list Specific seq 5 permit 172.16.1.0/24
!
route-map AS200-specific permit 10