Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
lacking. As illustrated by Wang et al., affinity purification of individual com-
ponents of protein complexes can be performed in an iterative fashion. Nanog-
associated proteins, either directly or indirectly, are predominantly either tran-
scription factors or others components of the transcriptional machinery. These
proteins include previously reported ESCs proteins, such as Oct4 and Dax1.
Through iterative purification of complexes following tagging of these proteins
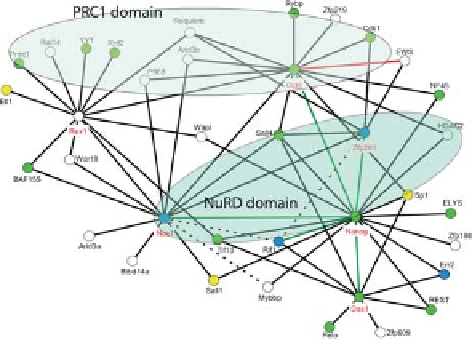
and others (Nac1, Zfp281, and Rex1) as second baits, a Nanog-related protein
network was generated (Fig. 1). The factors Sall4 and Dax1 have been identified
independently by other groups as involved in maintenance of ESCs pluripo-
tency (Elling et al., 2006; Niakan et al., 2006; Sakaki-Yumoto et al., 2006; Wu
et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006b). Interestingly, these proteins appear intercon-
nected with one another within a large network, suggesting that they function
cooperatively in control of gene expression. In addition, proteins of the network
are connected to transcriptional co-repressor complexes, such as the NuRD
(histone deacetylation) remodeling complex, histone deacetylases, and the
PRC1 (polycomb complex 1) (Fig. 1). Both complexes are recently reported
as required for pluripotency of ESCs (Endoh et al., 2008; Kaji et al., 2007).
These observations are consistent with a model in which proteins of the network
operate to silence differentiation as a means for maintaining the pluripotent
state. This network, a pluripotency ''interactome'', provides a framework for
exploring additional combinations of factors that permit faithful reprogram-
ming of differentiated cells to an ES cell state.
Fig. 1 Depiction of the
features of the interactome.
Green circles indicate
proteins whose knockout
results in defects in
proliferation and/or survival
of the inner cell mass or
other aspects of early
development; yellow circles
are proteins whose
knockout results in later
developmental defects
5 Extended Transcriptional Network: ChIP-ChIP
How do factors in the pluripotency network function to regulate downstream
genes? Genome-wide ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation) analysis can be
used now to predict target genes controlled by given transcription proteins.