Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The clinical significance of CSC population remains unclear. According to
CSC model, clinical success depends largely on the CSC population either in
quantitative terms such as the relative or absolute number of CSCs or qualita-
tive aspects related to biological features of CSCs. So far there are few data
addressing this question: a paper showing a higher percentage of CD34-CD38
blasts correlated with a poorer survival in acute myeloid form of leukaemia
(AML) (van Rhenen et al., 2005); another study showed that the percentage of
CD133-expressing cells in malignant brain tumours correlated with the rate of
tumour formation when implanted in immunodeficient mice (Bao et al., 2006).
On the other hand, certain natural properties of CSCs are likely to increase their
resistance to standard chemotherapy agents. In this connection, an intriguing
possibility is that CSCs express high levels of specific ABC drug transporters
(Fig. 3). Recently, ABCB5 was demonstrated to be expressed by a subset of
human melanoma cells (Frank et al., 2003). In physiological progenitor cells
ABCB5 functions to maintain membrane hyperpolarization, thereby serving
as a negative regulator of cell fusion of the expressing progenitor subset and
as a consequence of culture growth and differentiation (Frank et al., 2003).
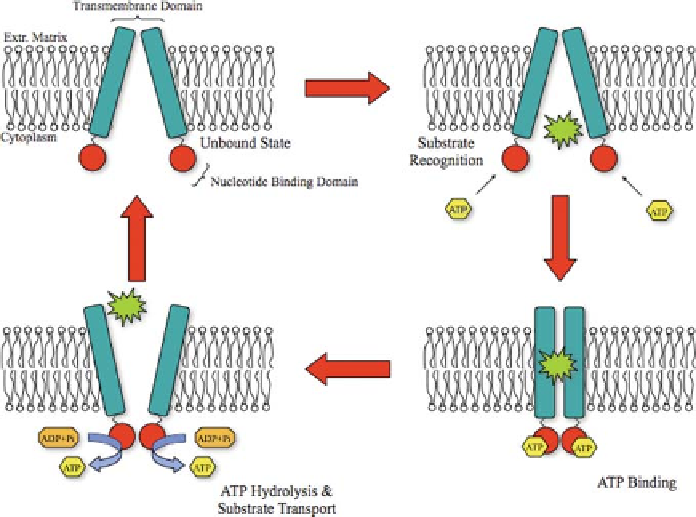
Fig. 3 ABC transporter molecules are responsible for ATP-dependent caring substances
(green) back and forth across the inner membranes of cells. In the inner part of the transporter
the hydrolysis of ATP through the ATP-binding domain induces conformational changes of
the ABC transporter. The ABC transporter is a large family comprising ABCG2 and ABCB5
molecules, both expressed in human melanoma cancer stem cells