Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
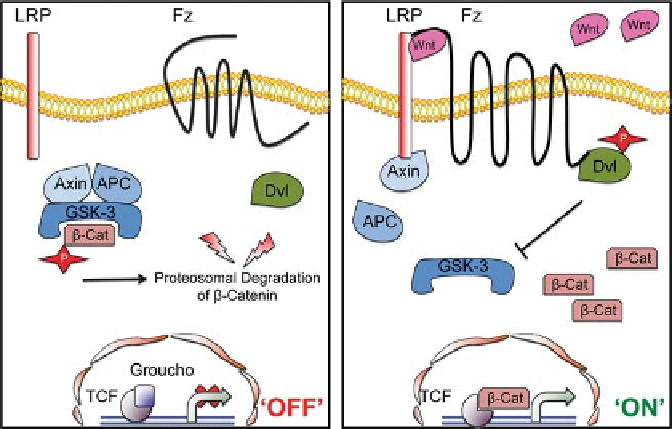
Fig. 1 The canonical Wnt transduction pathway.
Proteosomal degradation of beta-catenin via its phosphorylation occurs in the absence of Wnt
ligands. Downstream Wnt target genes are maintained repressed ('OFF '). Degradation of
active beta-catenin is reduced upon binding of Wnts. Accumulation and translocation of beta-
catenin into the nucleus leads to binding to T-cell factors and activation of target genes
('ON '). APC adenomatous polyposis coli, Dvl Disheveled, GSK glycogen synthase kinase,
TCF T-cell factor
the nucleus it binds to DNA-bound T-cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid enhancer
protein (LEF) family members to initiate the transcription of downstream target
genes. In the absence of the Wnt signal, the TCF/DNA-binding proteins form
a complex with Groucho and repress Wnt target genes (Cavallo et al., 1998),
(Nusse, 2005; Logan and Nusse, 2004). Groucho can interact with histone
deacetylases making the DNA refractory to transcriptional activation (Chen
et al., 1999a). Upon nuclear entry of beta-catenin into the nucleus, it competes
with Groucho for binding to TCF/LEF, recruits Pygopus, and converts the
TCF repressor complex into a transcriptional activator complex (Fig. 1). Target
genes include c-Myc, cyclin D1, MMP7, and WISP and a comprehensive list of
other Wnt target genes may be found on the Internet at
http://www.stanford.
edu/
rnusse/wntwindow.html
.
The Wnt pathway plays a critical role in lung carcinogenesis. Expression of
the Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1) has been shown to occur in the distal
epithelium of pulmonary airways; knockout experiments have shown that
Dkk-1 inhibits branching morphogenesis (De Langhe et al., 2005) and aberrant
Wnt pathway has been shown to have a role in non-small cell lung cancer