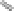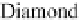Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
electrons is
U¼
0 (compared to
U¼j1
outside). In more common usage (see
Figure 3.13), the work function is measured above the Fermi energy, so that the
minimum energy for an electron in the interior, relative to the outside vacuum
energy, is
U
o
¼ðE
F
þjÞ:
ð
3
:
32
Þ
Returning to the work function value, it is reasonable that the work function
exceeds the cohesive energy
U
coh
because the former involves separating charge,
ionizing an atom. In a metal, the work function barrier arises from an electric dipole
layer. The electrons can tunnel slightly outside the perimeter of the metal ions, as we
have discussed in connection with Gamows probability and Figure 1.6, putting
negative charge outside themetal, whichwill then be compensated by positive charge
on inner side of the metal
-
vacuum boundary. This generates an electric dipole layer
that leads to a jump in electric potential, the work function barrier (see Figure 3.13).
Careful calculations of the work function for a wide range of metals have been
reported by Lang and Kohn [38], whose sketch of the surface dipole barrier is shown
in Figure 3.10. Their theory applied to gold gives work function values 3.5, 3.65, and
3.80 eV, respectively, for 110, 100, and 111 surfaces of the face-centered cubic crystal.
(The 111 surface is the body diagonal, 110 is the face diagonal, and 100 is the plane
face surface, see Figure 3.14.)
We now turn to diatomic molecules, starting with H
2
, but including atmospheric
gases, oxygen and nitrogen. These are held together by electron exchange, an effect
that is purely quantum in its nature, although the
final result is an electrostatic
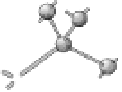
Figure 3.14 Diamond and zincblende crystal
structures. Each atom is covalently bonded to
four nearest neighbors in tetrahedral directions.
The directed bonds are linear combinations of s
and p orbitals (see Table 3.1), and analogous to
directed orbitals sketched in Figure 3.1.
Specifically, the linear combinations are 2s and
2p
3
for diamond (as in CH
4
) and 3s and 3p
3
for
Si. There are four valence electrons per atom,
leaving a band structure with filled bands, thus
insulating except for thermal excitations.