Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
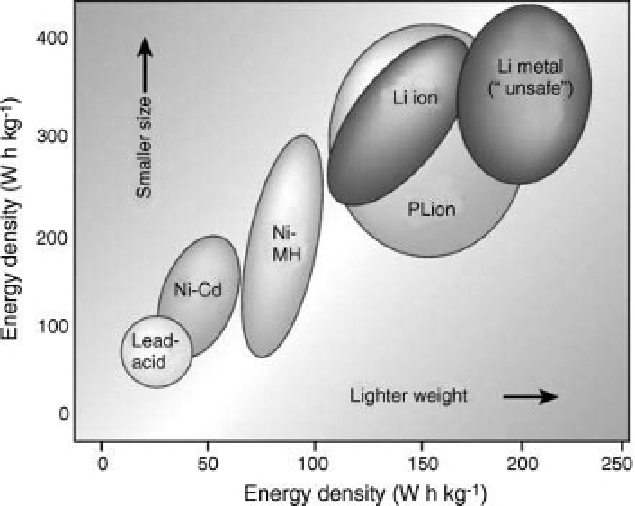
Figure 10.8 Comparison [140] of energy densities for several types of batteries. Units are watt
hours per liter (ordinate) and watt hours per kg (abscissa). Here, the label
PLiON
refers to a class
of rechargeable plastic Li-ion batteries.
about 63%, mostly in electronics, but not yet in hybrid cars. Ni
-
Cd batteries are used
in power tools.
The Prius hybrid car uses NiMH batteries, presently considered a more conser-
vative choice than the Li-ion battery, for which as shown in Figure 10.9 the graphite
electrode may present a
fire hazard. Nonetheless, an expensive roadster is being sold
by Tesla that is purely electric and powered by 6831 Li-ion cells of the type used in
laptop computers. This vehicle accelerates to 60 mph in less than 4 s and has a range
of 210 miles [141].
10.6.2
Basics of Lithium Batteries
A diagram of a lithium ion battery is shown in Figure 10.9.
Variations on the basic lithium battery shown in Figure 10.9 include a cathode of
iron phosphate LiFePO
4
[143] (manufactured by Lithium Technology Corp. and by
A123Sysems, which may involve nanoparticles) and possibly an anode consisting of
lithium titanate nanoparticles (Altairnano, Inc.) that will not burn.
It appears [143] that the electrical conductivity of the iron phosphate LiFePO
4
cathode (LFP), which had been low, was increased by doping with metals such as
aluminum, niobium, and zirconium, and also probably involving nanoscopic carbon
particles. These advances nowmake the iron phosphate cathode workable, to allow a
higher discharge current, fast charging time, and stability under extreme conditions.
The basic advantages of LFP cathodes over the cobalt cathodes are low cost, high