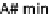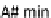Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5.11
A phrase generated by the Markov generator from the unique training phrase of
Fig.
5.10
. Phrases generated by diatonic scales are all Brownian by definition
Fig. 5.12
A phrase generated on top of an alternating
A min/A# min
chord sequence, using the
single ascending/descending A minor scale as training phrase. Note the two cases where no con-
tinuation is found to negotiate the chord changes (indicated by an
arrow
)
5.4.3 Chord Change Negotiation
Let us consider now a chord sequence based on alternating between
A minor
and
A# minor
. We deliberately choose
A# minor
as this key is 'far away' from
A minor
,
and therefore harder to 'negotiate', because these two scales share only a few notes.
Figure
5.12
shows an example of a phrase generated on this sequence. We notice
that there are two NSF cases. They correspond to situations in which the last note
of a phrase for a given chord does not exist in the training phrase for the next chord.
Here,
C#
does not exist in the training base for
A minor
(first case), and
B
does not
exist in the training base of
A# minor
, by definition of the harmonic minor scale.
Contrarily to general approaches to the
zero-frequency problem
, we propose a
musically justified solution with the two following arguments:
1. We reduce the number of NSF cases by carefully choosing the training corpus,
as detailed in the next section. This step corresponds to
human training
;
2. In the remaining (rare) cases no solution is found, we use a simple heuristic
based on the
one-step-max theorem
(see Sect.
5.2.3.2
): since there is always a
'good note' at a maximum pitch distance of one semitone, we try both and select
the one that works, and we are guaranteed that there is always one.
This double solution turns out to work nicely. It can be seen in Fig.
5.12
that in
both NSF cases, the system chooses the right notes a semitone apart to fit with
the harmony. The resulting phrase sounds smooth and continuous as if
nothing had
happened
: it is virtually impossible to notice that the generated phrase is locally
not Markovian. Furthermore, the system can easily produce a report after a series
of improvisations, to suggest adding a training phrase containing the NSF cases en-
countered. In our case it could suggest the musician/system to practise/add phrases