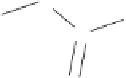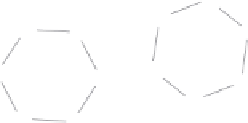Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
bond order (sometimes including aromaticity). To increase the level of chemical detail that
is considered, Kazius
et al
. used an extended chemical representation.
[
40
]
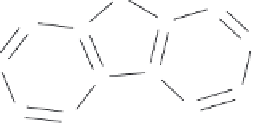
Figure 8.9 shows
a typical compound in standard chemical notation and two types of elaborate chemical
representation. Elaborate chemical representation uses atomic hierarchies in addition to
atom type labels, thereby including both general and more specific information. Atomic
hierarchies are tree-like structures that consist of a root of a general atom label represent-
ing an atomic property and branches of more atom-specific labels (specifiers). Aliphatic
nitrogen and oxygen atoms were labeled as 'small heteroatom' with specifiers for the atom
type and number of connected hydrogens, as shown in Figure 8.9 Aliphatic sulfur and
phosphorus atoms were labeled 'large heteroatom'with an additional specifier for the atom
type. Chlorine, bromine and iodine atoms were labeled 'halogen' with atom type specifiers
(Figure 8.9). For rings, two types of elaborate chemical representation were used. The
'aromatic' setting used a special atom label and bond type to represent aromatic atoms and
bonds and attached a type specifier to aromatic heteroatom. Examples of aromatic atoms
and bonds are shown in chemical representation
I
in Figure 8.9 The 'planar' setting used a
C
C
C
C
C
N
C
C
0
Cl
C
C
C
C
C
C
O
C
N
H
1
C
A
Cl
A
[N,O]
A
A
A
C
C
I
X
A
A
A
A
A
[N,O]
A
A
O
N
H
1
Pl
Pl
[N,O]
C
Pl
Cl
C
Pl
Pl
Pl
II
Pl
X
Pl
Pl
Pl
[N,O]
Pl
Pl
Pl
O
Figure 8.9
A typical compound (PubChem
1
CID78776) in standard chemical notation
(
0
)
and
two types of elaborate chemical representation, viz. the 'aromatic' setting
(
I
)
and the 'planar'
setting
(
II
)
. Bonds are either single, double, aromatic (gray double bonds in
I
) or planar (gray
single bonds in
II
). Additional information is attached using the dashed bonds. Atom labels
are carbon
(C)
, nitrogen
(N)
, oxygen
(O)
, small heteroatom
([N,O])
, halogen
(X)
, chlorine
(Cl)
,
aromatic atom
(A)
, planar atom
(Pl)
and number of implicit hydrogens
(
H
1
)
.