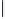Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
NH
2
NH
2
N
N
H
2
N
(CH
2
)
6-8
H
2
N
(CH
2
)
2-6
N
3
PZ6-8
PA2-6
N
3
HN
(CH
2
)
1-3
HN
(CH
2
)
2-6
⇔
N
N
TA1-3
TZ2-6
49 binary fragment combinations/98 potential triazoles
Scheme 7.6
Binary azide-acetylene fragment combinations with 98 potential triazole
products (including the
syn-
and
anti-
triazole regioisomers) for targeting AChE with
in situ
Click chemistry.
sample being required for the analysis. This analysis applied MALDI laser energies that
spanned from sub-threshold levels to above the threshold intensity for appearance of start-
ing material ions. The laser intensity applied was higher than used in conventional MALDI
or DIOS analyzes due to the presence of large amounts of protein in the samples. A single
hit compound was identified in this proof-of-concept study, namely triazole
syn-
TZ2PA6
(molecular weight
661 Da) formed by the reaction of fragments
TZ2
and
PA6
and the
presence of AChE. The DIOS mass spectrum demonstrating the formation of
TZ2PA6
is
shown in Figure 7.15. The assignment of this hit as the
syn
-regioisomer required authentic
synthesis of
syn-
TZ2PA6
and
anti
-
TZ2PA6
and determination of
K
d
values. The results
demonstrated that only
syn-
TZ2PA6
was formed in the presence of AChE. A remarkable
finding is that this compound was the most potent noncovalent AChE inhibitor reported
to date, with
K
d
values of 77 fM (eel AChE) and 410 fM (murine AChE). In contrast,
the
anti
-
TZ2PA6
isomer is not formed by the enzyme and is less active by two orders of
magnitude. These first experiments also demonstrate that the
in situ
experiment avoided
the requirement to synthesize all 98 possible triazoles; instead, the synthesis of just two
triazoles was required.
It was clear from this early work that mass spectrometric analysis would be the most
appropriate technique to detect hit compounds for
in situ
Click chemistry applications.
Although the DIOS-MS method was able to directly detect the low quantity of triazole
product conversion in the presence of large amounts of protein and parent fragments, the
sensitivity for this measurement was very low, with a poor signal-to-noise ratio. It was
therefore both logical and desirable to optimize the sensitivity and selectivity of the MS
=