Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a.
0123456789012345601234567890123456
+--+?aa?aaa655501-a+?-?aaa??577
+--+?aa?aaa655501-a+?-?aaa??
250
250
772
C = {-0.273, -0.376, -1.089, -1.544, -0.668, 1.969, -1.978, -1.192, -1.930, 0.053}
C = {1.499, -0.346, 0.391, -0.232, 0.307, 1.586, -0.300, 0.729, -0.885, -0.1897}
1
2
b.
Sub-ET
1
Sub-ET
2
a
a
a
-1.978
1.586
a
a
1.969
0.729
c.
Sub-ET
1
Sub-ET
2
a
a
a
-1.978
0.391
a
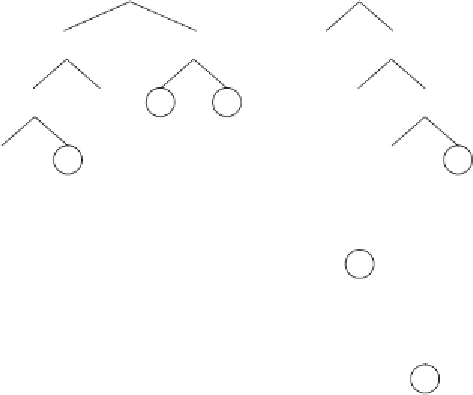
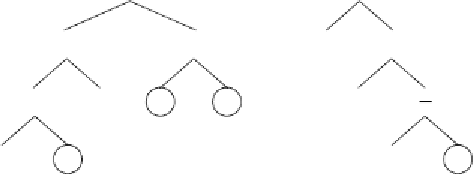
Figure 5.6.
Illustration of Dc-specific transposition.
a)
The mother and daughter
chromosomes with their random numerical constants (the RNCs are exactly the
same for both mother and daughter and therefore are shown just once).
b)
The sub-
ETs encoded by the mother chromosome (before transposition).
c)
The sub-ETs
encoded by the daughter chromosome (after transposition). The nodes affected by
transposition are highlighted. Note that not only a new constant is expressed in
the daughter tree but also a different interaction is being tested for constant 1.586.
a
1.969
1.586
occurred in C
2
, changing the number 0.218 at position 5 by 0.853 and -0.770
at position 7 by -0.256, giving:
0123456789012345601234567890123456
**a//aa?a??461226*a+*?a?aaaa406961
(5.13)
C
1
= {0.139, -0.299, -1.024, -0.330,
-0.256
, -1.864, 1.008, -0.712, -1.740, 1.552}
C
2
= {-0.986, -0.147, -1.113, -1.577, 0.210,
0.853
, 1.705,
-0.256
, 1.845, 1.954}