Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a.
012345678901234567890012345678901234567890
OAaOaAa aaabccccbAAbObAObAAababcacccab-[m] = 7
OAaOa aaabccccbAAbObAObAAababcacccab-[d] = 8
AcAaa
AcAaa
aa
b.
Sub-ET
1
Sub-ET
2
O
A
A
a
A
b
a
O
b
O
a
A
A
O
c
A
b
A
A
a
a
a
c
A
b
b
a
a
c.
Sub-ET
1
Sub-ET
2
A
A
c
A
A
b
a
a
a
O
A
O
a
b
A
A
a
c
b
b
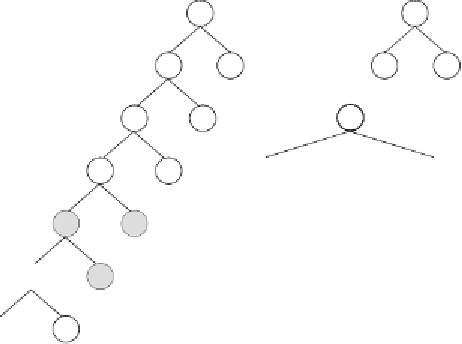
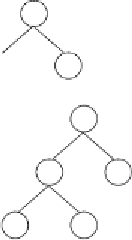
Figure 3.21.
Illustration of RIS transposition and its effects.
a)
An event of RIS
transposition with the transposon shown in bold. Note that a sequence with the
same length as the transposon is deleted at the end of the head of the target gene.
Note also that the transposon became, in this case, only partially duplicated in the
daughter chromosome as its other elements disappeared at the end of the head.
b)
The sub-ETs encoded by the mother chromosome (before RIS transposition).
c)
The sub-ETs encoded by the daughter chromosome (after RIS transposition)
(the transposon elements are shown in gray). Note that, in this case, root transpo-
sition changed drastically the sub-ET
1
, shortening the daughter sub-ET in eight
nodes and making it a better adapted individual in the process.