Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6
6
i
A
i
B
i
C
i
A
−i
a
i
B
−i
b
i
C
−i
c
4
4
2
2
0
0
−2
−2
−4
−4
−6
−6
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
Time [s]
Time [s]
(a) Inverter currents (b) Load currents
30
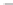
6
u
A
u
B
u
C
i
a
i
b
i
c
4
15
2
0
0
−2
−15
−4
−30
−6
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
Time [s]
Time [s]
(c) Local load voltages
(d) Grid output currents
10
5
THD of i
a
=5.54%
THD of u
A
=1.78%
4
3
5
2
1
0
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Harmonics order
Harmonics order
(e) Spectra of the local load voltage
(f) Spectra of the grid output current
Figure 18.13
Loading performance in the grid-connected mode with an unbalanced local load
18.6 Summary
Based on (Zhong and Weiss 2009, 2011), the idea of operating an inverter as a synchronous
generator is developed in this chapter after establishing a model for synchronous generators
to cover all the dynamics without any assumptions about the signals. The implementation and
operation of such an inverter, including power regulation and load sharing, are developed and
described in detail. The mathematical model developed here can be used to investigate the
stability of power systems dominated by parallel-operated inverters in distributed generation.
Both simulation and experimental results are provided.





























































































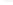






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search