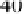Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
ketchup, mustard, etc. In contrast if the sign for cross price elasticity of demand is positive,
the goods are substitutes for each other. One classic example is Coke and Pepsi. If the price
of Pepsi is higher, the demand for Coke will increase. Finally, if the sign is near zero, it
means that the demand for one good does not depend on the price change in another good.
For example, the demand for coffee will not change if ketchup is put on sale.
Summary
Agribusiness managers must have a clear understanding of economics to be successful.
Economics involves the allocation of scarce resources, that is, land, labor, capital, and man-
agement, to meet the needs of society. Macroeconomics focuses on a “big picture” view of
our economic system. Microeconomics is the application of basic economic principles to
decisions within the fi rm.
The profi t motive is used as an incentive that guides businesses in fulfi lling consumer
wants as consumers express these wants in the marketplace with their dollars. Several eco-
nomic concepts provide insights for agribusiness managers. Opportunity cost is the income
given up by not choosing the next best alternative for the use of resources. Economic profi t
is defi ned as accounting profi t less opportunity cost. Economic profi t then forces managers
to explore alternative uses of resources.
Supply captures the relationship between price and quantity supplied. Demand curves
slope downward from left to right, indicating that larger quantities are only purchased at
lower prices. Applying supply and demand principles is important in understanding how
markets work, and how prices move. Elasticity estimates for demand help agribusiness man-
agers examine the potential impact of changes in price, income, or other prices on quantity
demanded.
Discussion questions
1.
Why should agribusiness managers be interested in macroeconomics? Give a specifi c
example of one macroeconomic development and describe the impact of this develop-
ment on the food and agribusiness industries.
2.
What is your opportunity cost associated with attending college? Be specifi c.
3.
Consider the supply of milk. What are at least three different developments that might
shift the supply curve for milk? Be specifi c.
4.
Consider the demand for frozen yogurt. What are three different developments that
might shift the demand curve for frozen yogurt? Be specifi c.
5.
How might the marketing manager of an agribusiness fi rm use elasticity of demand
coeffi cients? Be specifi c .
Case study: Armstrong Agribusiness, Inc.
A local agribusiness enterprise has employed a consultant to estimate its supply curve for a
specifi c tractor part and to estimate the demand faced for this part in its local marketplace.
The consultant has determined the following:
Demand
Q
P
:
SupplyQ
P
40
2
=+