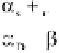Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
of prices and quantities called a demand and a supply schedule (
Table 3.2
). For each price,
demand is the total quantity sold, while the total quantity produced represents what a fi rm
will supply.
Second, supply and demand is commonly shown graphically, as in
Figure 3.1.
Third, the
supply and demand curves from
Figure 3.1
c
an also be expressed as an algebraic function of
prices and quantities, or
()
P
α
β
s
α
β
D
Q
s
s
s
()
P
Q
DDD
where:
Qis quantity supplied,
s
Q s
quantity demanded,
q
price, and and
D
P =
b
are parameters tha
t indicate the relationship between
α
the variables P and Q..
In this case, the upward sloping supply curve for equation (1) is P = 5 + 1Q
S
, while the down-
ward sloping demand curve for equation (2) is expressed as P = 92.5 - 2.5Q
D
.
The process of price discovery means that market equilibrium for quantity and price is
determined (or discovered) through transactions between producers and consumers. Only
one price and quantity will “clear the market” at a given point in time. At equilibrium, every-
thing that producers are willing to sell will equal everything that consumers want to buy.
Thus, at market equilibrium the quantity demanded is simply equal to the quantity supplied.
and the quantity (Q
1
) of 25,000 cases. Alternatively, simultaneously solving equations
(1) and (2) gives the same result.
The textbook version of supply and demand is seldom encountered. Rather than having
the theoretical supply and demand curves as in
Figure 3.1,
fi rms typically only have a hand-
ful of observations of prices and quantities. For example, a fi rm may have only three points
of information (A, B, and C) instead of a complete supply curve, and no formal estimate of
a demand curve (
Figure 3.2
). Yet even with only one point, the concepts of supply and
demand are understood and used in decision-making.
Table 3.2
Demand and supply schedules for cereal
Price per case ($)
Total quantity sold
(1,000 cases per month)
Total quantity produced
(1,000 cases per month)
20.00
29
15
22.50
28
18
25.00
27
20
27.50
26
23
30.00
25
25
32.50
24
28
35.00
23
30
37.50
22
33
40.00
21
35