Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Manager
Assistant
manager
Office manager/
Accountant
Horticulturalist
Greenhouse
manager
Nursery
manager
Retail store
manager
Assistant
nursery
manager
Field
hands
Delivery
persons
Worker
Worker
Mechanic
Worker
Worker
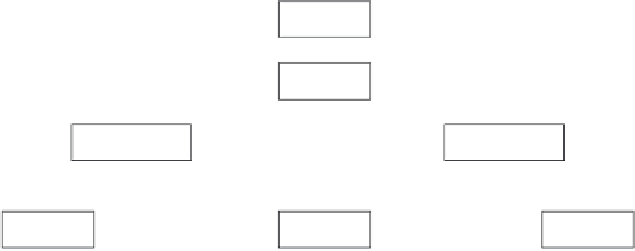
GreenThumb, Inc.
Line and staff organizational chart
5th year
Figure 16.2
Line and staff organization
may feel so strongly about a particular issue that they may apply pressure or go around the
normal chain of command. If GreenThumbs's horticulturalist tells nursery workers to begin
treating growing beds with insecticide, such a request may be in direct confl ict with the
nursery manager's established work schedule, creating much confusion among employees
and ill feelings with management.
Functional organization
A
functional organizational structure
meets the problems of staff specialists' authority
head-on by granting them authority in the areas of their specialty (
Figure 16.3)
. The horti-
culturalist that sees the need for an immediate insecticide treatment of bedding plants has the
responsibility and the authority to command workers to make the application.
Of course, a functional organization offers an almost unlimited potential for confl ict and
confusion. Who has the highest authority? From whom do workers really take orders? The
key to making the functional structure work is coordination of staff and line management
efforts. A cooperative attitude and good communication are absolutely essential for this
organizational structure to work. While complex, this organizational structure, or a variant,
is very common in agribusinesses, especially larger ones. Such businesses have found that
the advantages of functional organization outweigh the disadvantages.
Communication: the key to success
No matter how well thought-out the organizational structure, there will be times when it
breaks down. Agribusinesses, large and small, are complex operations that do not always