Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
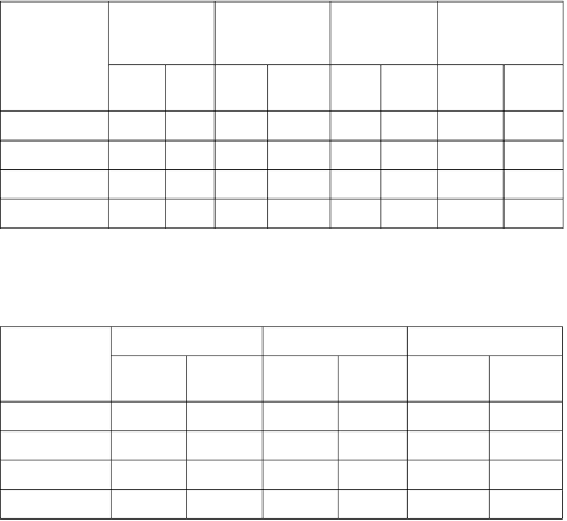
Table 29
Changes in yield components with the day in transplanting.
Date of
transplanting
No. of
Panicle per
hill
No. of Filled
grains per
panicle
Spikelet
sterility (%)
1000 grain
wt.(g)
BD
46
BD
31
BD
46
BD
31
BD
46
BD
31
BD
46
BD
31
Sep 01
16.5
15.5
125
120
13.5
11.5
26.0
27.0
Sep 10
17.0
13.0
115
105
14.5
15.5
26.0
26.5
Sep 20
14.0
12.0
110
90
15.4
17.4
23.5
23.0
Sep 30
12.5
8.0
105
81
17.0
24.0
23.0
20.0
CV. BD46 and BD31
Table 30
Yield and harvest index of rice varieties as affected by transplanting
dates.
Date of
transplanting
Grain yield (tha
-1
)
Straw yield (tha
-1
)
Harvest index (%)
BD
46
BD
31
BD
46
BD
31
BD
46
BD
31
Sep 01
4.50
4.90
7.60
9.80
37.19
33.33
Sep 10
4.30
4.60
8.25
9.76
34.26
32.03
Sep 20
4.10
3.90
7.54
7.65
35.22
33.77
Sep 30
3.80
3.10
6.70
6.40
36.19
23.63
The Korean peninsula is located in the Far East, between
latitudes 33º06' and 43º01' north between longitudes 124º11; and
131º53' east, in the northern temperate climate zone. Summers
are hot and humid and winters severely cold. Rice is therefore
a summer crop, grown between April and October. In the
northern mountain regions, the rice plant can suffer from low
temperatures at any stage between germination and maturity.
In years of extreme low temperatures, all rice growing area as
are susceptible to cold at the reproductive stage. For example,