Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Clearly
2<p<2, otherwise this relation cannot hold for both signs of the
square root. Notice that (F.3) is equivalent to
p
p
2
4q < min
f
2
C
p;2
p
g
;
or equivalently
p
2
4q < min
f
4
C
4p
C
p
2
;4
4p
C
p
2
g
;
which can be rewritten as
1
C
p
C
q>0 and 1
p
C
q>0:
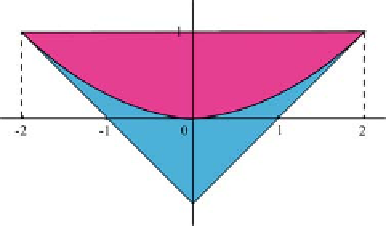
The cases of real and complex roots are shown in Figure F.1. The assertion can
be obtained by combining the two cases.
Consider next a real matrix
ab
cd
;
the characteristic polynomial of which is
'./
D
.a
/.d
/
bc
D
2
.a
C
d/
C
.ad
bc/:
Let Tr
D
a
C
d denote the trace and
Det
D
ad
bc the determinant of this
matrix, then
'./
D
2
Tr
C
Det
:
The eigenvalues of this matrix are inside the unit circle if and only if
q
Complex roots
p
Real roots
Fig. F.1
The stability region (shaded) of the quadratic polynomial (F.1) in the .p;q/ plane. It
shows the bounding lines 1
q>0and q<1. Also shown are the regions
where the roots of (F.1) are real and where they are complex, with the boundary between the two
regions being the parabola q
C
p
C
q>0, 1
p
C
p
2
=4.
D

Search WWH ::

Custom Search