Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
the firm to learn the true value of the slope of the market demand. If the expression
on the left hand side of (5.103) is increased past the value 2, then the fixed point
loses its stability via a flip (or period doubling) bifurcation, at which a stable cycle
of period two is created around it.
However, in order to understand the global dynamical properties of the one-
dimensional map (5.102), the graph of g."/has to be examined for ">0.Itis
a hyperbola with a vertical asymptote at "
D
0
C
,andfor"
!C1
it approaches
the asymptote given by the equation
1
"
C
Aa
.N
C
1/B
a.A
Nc/
N
C
1
y
D
:
(5.104)
Aa
B.N
If
1/
>1then the map g is decreasing, and for "
!C1
it tends to
1
along
the negatively sloped line (5.104). In this case, any positive trajectory converges to
the steady state if the stability condition (5.103) is satisfied, whereas if (5.103) does
not hold a stable cycle of period two may be the unique attractor: no other different
kinds of attractors can exist for a decreasing map. On the other hand, if
C
Aa
B.N
1/
<1
C
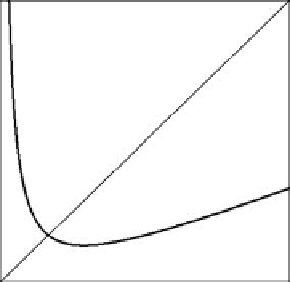
then the map g is unimodal (see Fig. 5.5a). It decreases for "<"
min
,where
s
Nac
.N
C
1/B
Aa
;
"
min
D
B
and it increases for ">"
min
.As"
!C1
it approaches the positively sloped line
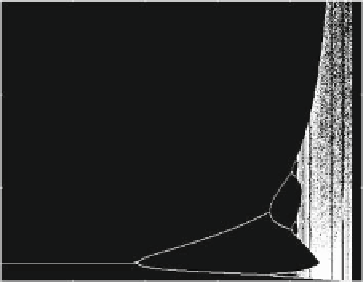
(5.104). This case may give rise to more complex dynamic properties. In fact, in this
case the first period doubling bifurcation at which the steady state loses stability
30
ε
g
(
e
)
g
2
(
e
min
)
g
(
e
min
)
e
e
min
0
a
/
B
(a)
(b)
Fig. 5.5
Oligopoly with N identical firms starting from identical initial guesses on the scale factor.
(
a
)Themapg and the trapping region of the dynamics. (
b
) Bifurcation diagram with respect to the
parametric ratio a=B,wherea is the common speed of adjustment of the firms and B is the slope
of the demand function. Here N D 3, A D 3, B D 2 and c D 2









Search WWH ::

Custom Search