Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
R
k
.Q
k
/
L
k
Q
k
P
i ¤k
L
i
A
c
k
B
Fig. 1.4
Example 1.2; the Cournot model with linear price function and quadratic cost function
in the case of duopoly .N
D
2/. The figure shows the reaction function of a typical firm in case
(iii) when e
k
D
B. The number of equilibria may be 1;3 or infinite
the two straight lines either coincide or are parallel. Therefore there are either
infinitely many equilibria, or a unique boundary equilibrium.
(iii) In the case where e
k
D
B for all k, the profit function assumes the linear
form
'
k
D
x
k
.A
BQ
k
c
k
/;
therefore
8
<
0
if A
BQ
k
c
k
<0;
R
k
.Q
k
/
D
L
k
if A
BQ
k
c
k
>0;
:
if A
BQ
k
c
k
D
0:
arbitrary x
k
We can assume again that c
k
<A,otherwiseR
k
.Q
k
/
D
0 for all Q
k
.Thisbest
response function is illustrated in Fig. 1.4 in the case when
<
X
i
A
c
k
B
L
i
:
¤
k
In the case when the last inequality becomes an equality, the vertical seg-
ment moves to Q
k
D
P
i ¤k
L
i
. If however the above relation is violated with
strict inequality, then R
k
.Q
k
/
D
L
k
for all Q
k
. Depending on the values of
.A
c
k
/=B and L
k
, in the duopoly case the number of equilibria can be 1, 3
or infinite; Fig. 1.5 shows a case where three equilibria exist.
(iv) Assume finally that for all k, e
k
<
B. In this case '
k
is convex in x
k
,sothe
best response is located at an endpoint of the feasible interval [0;L
k
] and is of
the form
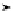


Search WWH ::

Custom Search