Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
1.1
1.6
L
E
′
L
b
1
E
D
(2)
D
(3)
x
2
x
2
b
1
b
2
D
(2)
D
(1)
D
(1)
b
2
x
1
L
0
0
x
1
1.1
L
1.6
(a)
(b)
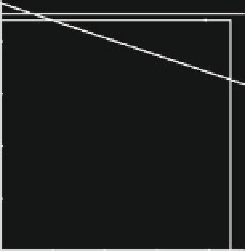
Fig. 4.9
Example 4.6; the discrete time model of an N-firm labor-managed oligopoly in the semi-
symmetric case. Linear price function and quadratic labor unit functions. (
a
) The phase space for
L
D
1.(
b
) The phase space for L
D
1:5
1.7
1.9
L
L
b
1
D
(2)
E
D
(2)
b
1
x
2
x
2
E
2
b
2
E
1
E
1
D
(1)
D
(1)
x
1
x
1
0
L
1.7
0
L
1.9
(a)
(b)
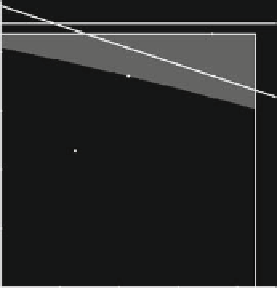
Fig. 4.10
Example 4.6; the discrete time model of an N-firm labor-managed oligopoly in the
semi-symmetric case. Linear price function and quadratic labor unit functions. (
a
) Co-existence of
interior equilibria and their basins of attraction for L
1:8 the second co-existing
equilibrium E
2
has disappeared and E
1
becomes the unique and globally stable attractor
D
1:55,(
b
)AtL
D
two basins is given by the sta
ble set of
the
sa
ddle point E
2
. A further increase of L
above the bifurcation value
p
d
1
C
d
2
D
p
3 marks a remarkable qualitative change
in the global dynamic scenario: the boundary equilibrium E and the saddle point
E
2
disappear (they exit the respective regions
.2/
after merging along
the boundary) and the interior equilibrium E
1
remains the unique (and globally sta-
ble) attractor (see
Fig
. 4.10b obtained for L
D
1:8). This explains the sudden jump
.1/
D
and
D
occurring at L
D
p
3 in the bifurcation diagram of Fig. 4.8.


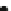




Search WWH ::

Custom Search