Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
1
1
x
'
2
LC
(
a
)
x
2
Z
0
(
a
)
LC
−1
Z
2
(
b
)
LC
−1
x
1
1
K
LC
(
b
)
Z
4
0
1
0
1
x
1
x
'
1
(a)
(b)
x
'
2
x
2
Z
0
LC
(
a
)
(
a
)
LC
−1
Z
2
LC
(
b
)
(
b
)
LC
−1
Z
4
0
x
1
0
x
'
1
(c)
Fig. 3.13
Oligopolies with linear inverse demand function and cost externalities, the case of
duopoly with identical speeds of adjustment. (
a
) The two disjoint branches, LC
.a/
1
and LC
.b/
1
of the curve LC
1
.(
b
) The critical curves LC
D
T.LC
1
/. Note the cusp at K.(
c
) Illustrating
the Riemann foliation of the .x
1
;x
2
/ plane
a higher number of preimages then before. The unfolding process of the inverse of
the map T then causes the creation of disconnected components of the basins. The
bifurcation occurring at a.
C
1/
D
1 is a
global (or contact) bifurcation
,which
is characterized by a contact between the stable set of E
S
along the diagonal
and a critical curve LC. The coordinates of the cusp point of LC
.b/
can be easily
computed in our case. Using (3.27) it is easy to see that the intersection of LC
.b/
1
with the diagonal occurs at
a.
C
1/
1
2a
K
1
D
LC
.b/
1
\
D
.k
1
;k
1
/ with k
1
D
:












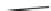















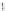















Search WWH ::

Custom Search