Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
aT
(
aT
)
2
*
1
(
aT
)
1
*
r
-1
−8
N-
1
0
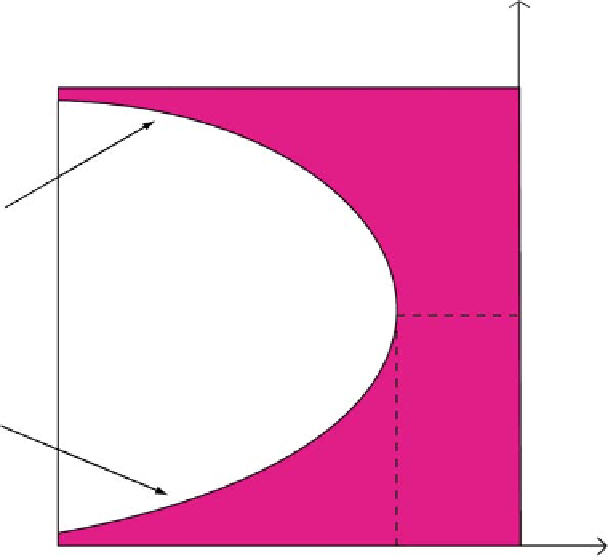
Fig. 2.20
Stability region in the .r;aT/-space for continuous time symmetric oligopolies with
time delay in information about rival firms
between .aT/
1
and .aT/
2
, then it is unstable. So with fixed value of r,ifaT is
gradually increased from a very small value and crosses .aT/
1
, then asymptotic
stability is lost. This instability holds until the value of aT reaches .aT/
2
,and
on crossing this value, asymptotic stability is regained. It is very interesting to see
what happens at these critical values .aT/
1
and .aT/
2
. We will show that a Hopf
bifurcation occurs (see for example, Guckenheimer and Holmes (1983)) giving the
possibility of the birth of limit cycles around the equilibrium as aT crosses these
critical values.
In fact we may state the following theorem concerning a Hopf bifurcation in the
m
D
1 case:
Theorem 2.3.
In the case of
m
D
1
the dynamics of the symmetric oligopoly loses
local asymptotic stability and a Hopf bifurcation occurs as
aT
crosses the critical
value
.aT/
1
from below and the critical value
.aT/
2
from above.
Proof.
We select T as the bifurcation parameter, and consider the roots of the
eigenvalue equation (2.59) as functions of T ,thatis
D
.T/. In order to show that
a Hopf bifurcation occurs we have to prove two facts. First, that at the critical value
Search WWH ::

Custom Search