Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
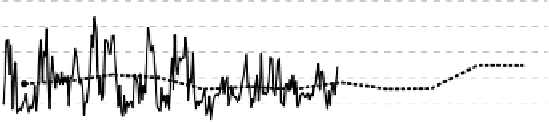
two hourly course curves on the basis of mean wind speed valued per minute (for
the 12
th
hour respectively) are shown. Accordingly, the wind velocity at this site is
characterised by a weak annual course. The mean hourly wind speed values and
the velocities per minute, in contrast, are only characterised to a very limited ex-
tent by a typical course.
10
10
8
8
Hourly cycle
6
6
4
4
Hourly cycle
2
2
0
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
Time in minutes
Time in minutes
10
10
8
8
Daily cycle
6
6
4
4
Daily cycle
2
2
0
0
0
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
0
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
Time in hours
Time in hours
10
Annual cycle
8
6
4
2
0
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
240
270
300
330
360
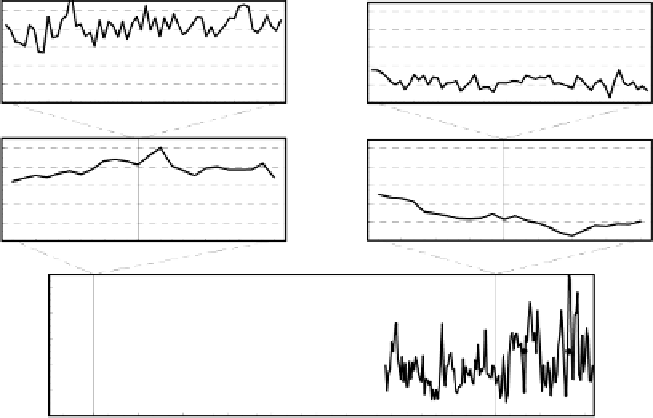
Fig. 2.30
Annual, daily and hourly courses of wind velocities for the example of a site in
North Germany (see /2-7/)
Time in days
The diagram also shows the large variations of the mean daily, hourly and min-
ute wind velocities during the given period of time. If, for example, the variations
of the mean minute wind speed were analysed with regard to the mean hourly
value, variations between +/- 30 and 40 % would be obtained.
Similar curves will also be found for other sites throughout the globe, but very
high variations may occur. For example, the order of magnitude of the measured
wind speed might vary according to the local given situation at the measuring spot
and the investigated height above ground, among other factors. The wind speed is
also very much controlled by micro-meteorological conditions (i.e. stable or un-
stable weather conditions).
The fact that, for instance, the annual cycle of the wind speed is subject to sig-
nificant fluctuations is also shown in Fig. 2.31. This graphic displays the monthly
average wind speeds at Helgoland Island/Germany, Kuala Lumpur/Malaysia,
Wellington/New Zealand, Lanzarote/Canary Islands/Spain and Buenos Ai-
res/Argentina. According to these data all annual cycles of the wind speed dis-
played show more or less pronounced seasonal differences. The wind velocities
on the island of Lanzarote, for example, reach their maximum during summer
time and fall off in winter.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search