Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
These contexts show that the radiation is composed of a deterministic and a
stochastic element. The former is the radiation component that is always present
(i.e. the proportion of diffuse radiation incident during the course of the entire day
when the sky is completely overcast). The latter describes the proportion between
the deterministic component and the maximum possible radiation (i.e. the maxi-
mum possible radiation at a completely clear sky during the entire course of the
day) that is likely to occur to a certain extent. Both components vary depending
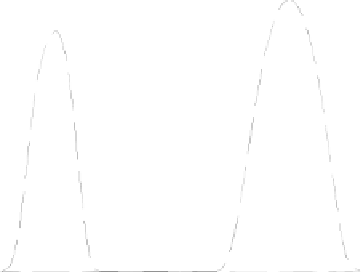
on the season and the time of day. Fig. 2.19 shows schematically the course of the
minimum and the maximum possible mean hourly radiation intensity (i.e. the ra-
diation intensity at a completely clear or completely overcast sky) for the days of
winter and summer solstice at a site in Central Europe. Furthermore, the graphic
contain an exemplary possible course of solar radiation intensity. According to
that, the spectrum within which the solar radiation can fluctuate during daytime
hours is very high. On the other hand, the substantial influence of the cloud
amount on the solar efficiency becomes apparent.
Winter day
Summer day
900
The
o. min. val
ue
Act u al v al u e
The
o. max. va
lue
800
700
600
Stochastic
share
500
400
300
Deterministic
share
200
100
0
4
8
12
16
20
4
8
12
16
20
Time in hours (GMT)
Time in hours (GMST)
Fig. 2.19
Deterministic and stochastic part of solar radiation (Theo. theoretical, min.
minimum, max. maximum) (see /2-7/)
Thus the hourly radiated power is deterministic and predictable within certain
boundaries. However, within these boundaries which can be very far apart from
each other depending on the time of the day or the year, the radiation supply is
mainly stochastic. The stochastic character of solar radiation is significantly influ-
enced by the current macro and micro-meteorological conditions. These variations
are therefore interdependent at different points in time that lie closely together.
Thus the cloudiness at a certain point in time has a significant influence on how
overcast the atmosphere is going to be in the following hour. This influence de-
creases with an increasing time distance. This is also true for the space depend-
ency. Cloudiness at different, geographically close sites is coupled - dependent on




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search