Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Space
heating
Space
heating
Evaporator
Heat pump
Compressor,
condensor
Heat store
Heat store
sdf
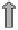
Fig. 9.6
Heat pump using ambient air as heat source (left: outdoor installation; right: split
installation)
−
Indoor installation. Another form of installation is the complete integration of
the heat pump into the building (Fig. 9.7). In that case the ambient air has to be
transported to the heat pump through air ducts that are insulated well against
heat and noise. The cooled down air then has to be discharged again to the en-
vironment. Intake and outlet opening have to be built in a way that avoids a
"shortcut" between the cooled down exhaust air and the intake air.
Space
heating
Air ducts
Heat pump
Heat store
Fig. 9.7
Heat pump using ambient air as the heat source (indoor installation)
Flat-plate absorbers with integrated evaporator tubes combine the utilisation of
ambient air and solar radiation. Often a brine circuit is installed between the ab-
sorber and the evaporator, as the oil recirculation into the refrigerant circuit is not
ensured in the case of flat-plate absorbers. As flat-plate absorbers use diffuse and
direct solar radiation, the location and the direction are important. Additionally,
there has to be a way of releasing the condensate created by the absorber.
A special form of ambient heat exchanger, which belongs to the group of flat-
plate absorbers are, the solid absorbers. The heat exchanger tubes of this absorber

















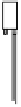













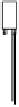


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search