Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
the transparent cover needs to be cleaned as room air and heated air tend to min-
gle.
Solar wall systems or indirect gain systems are suitable to complement direct
gain systems, since, when combined, they extend heat distribution into the living
space. Combinations of both systems are particularly appropriate for living spaces
with continuous heat demand.
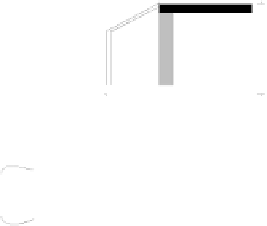
Solar wall
Solar wall with glass extension
Solar wall with convection support
Fig. 3.8
Different types of solar wall systems (see /3-8/)
Transparent thermal insulation.
Besides the direct utilisation of solar radiation by
windows, within the last few years, also wall systems equipped with transparent
thermal insulation (TI) have been developed to enhance passive solar energy
gains. They are a special variant of indirect gain systems, as they enable the effec-
tive utilisation of passive solar systems in Central Europe thanks to the use of
transparent heat insulators.
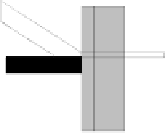
TI-material
Solar radiation
Solar radiation
Heat gain
Heat gain
Heat loss
mainly by
diffusion and
reflection
Heat loss
mainly reflection
Thermal storage
wall
Solid wall
Absorption surface
Insulation
Air gap, if applicable
Fig. 3.9
Comparison of opaque (left) and transparent thermal insulation (right)
Only very little of the solar radiation incident on an opaque thermal insulation
can be utilised (Fig. 3.9, left). During absorption of solar radiation the outer sur-
face may heat up; however, due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search