Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
80
Lucerne
60
Grass
40
Red clover
20
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Time in months
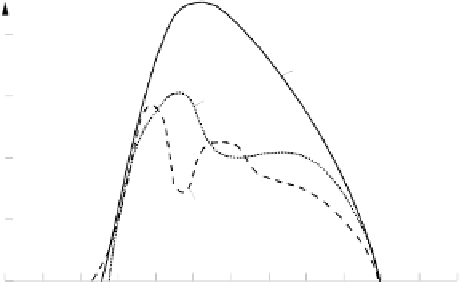
Fig. 2.53
Biomass growth increment of various forage crops in the course of the year ex-
emplarily for sites in Central Europe (see /2-32/)
2.6
Geothermal energy
Apart from the energy resulting from solar energy and the interaction of planet
gravitation and planet motion, the heat stored in the earth is another renewable
energy source available to human mankind. In the following chapter the principles
of this type of energy supply are described and discussed.
2.6.1
Principles
Structure of the earth.
Earthquakes cause sound waves occurring as compres-
sions of matter (compression waves) or as movements perpendicular to the direc-
tion of propagation (so-called shear waves). They can be measured with receivers
(seismometers) distributed throughout the overall globe. By tracing and analysing
these sound waves, a layered structure of the earth can be determined.
Table 2.6
Physical properties in the interior of the earth
Depth
in km
Density
in kg/dm
3
Temperature
in °C
Earth's crust
Earth's mantle
Earth's core
0 - 30
up to 3,000
up to 6,370
2 - 3
3 - 5.5
10 - 13
up to 1,000
1,000 - 3,000
3,000 - 5,000
The crust of the earth, or the top layer, reaches below the continents to a depth
of approximately 30 km; below the oceans the earth crust only has an average



Search WWH ::

Custom Search