Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
transport in HEC-RAS is based on shear stresses computed from these steady state
events. However, the interaction of the bed profile with the entrainment and
transport equations is quasi-dynamic in that the bed is adjusted for erosion or
deposition by the Exner equation. Sediment transport module simulates suspended
load (fine sediments moving at the same speed as water) and bedload (sand and
gravel moving at a slower rate along the bed). Seven different transport functions
are currently available in RAS including Ackers and White, Englund-Hansen,
Laursen, Myer-Peter-Muller, Toffaleti, Yang, and Wilcock. Currently HECRAS
employs Exner 5, a ''three layer'' algorithm to compute bed sorting mechanisms.
Exner 5 divides the active layer into two sublayers, simulating bed coarsening by
removing fines initially from a thin cover layer. During each time step, the
composition of this cover layer is evaluated and if, according to a rough empirical
relationship, the bed is partially or fully armored, the amount of material available
to satisfy excess capacity can be limited.
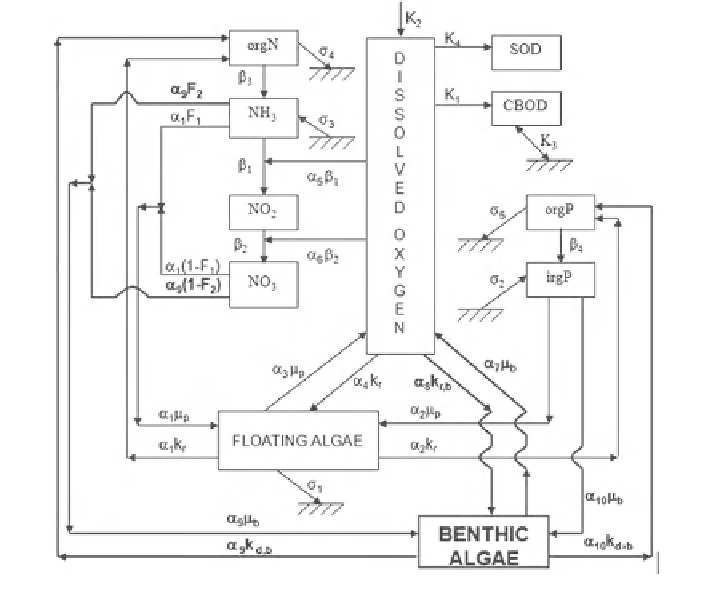
HEC-RAS nutrient water quality module includes a set of nutrient simulation
modules (NSM) (Zhang and Johnson
2012
). NSM I computes riverine algal bio-
mass, organic and inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus species, CBOD and DO.
NSM II computes multiple algal biomass, nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon
cycling, DO, COD, alkalinity, pH and pathogen, as well as numerous additional
Fig. 10.5
Schematic representation of HEC-RAS-NSM I
Search WWH ::

Custom Search