Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
12.3.2 Numerical results
In the following application a 4D computed tomography (CT) dataset of a human
aorta was employed as image source. The dataset was acquired at Ospedale Mag-
giore in Milan (Italy) using a Siemens SOMATOM Definition Flash Dual-Source
CT scanner, which was able to capture 10 time frames per cardiac cycle. The 4D im-
age refers to a 72-year-old man with a diagnosed abdominal aneurysm and covers the
entire length of the ascending, thoracic and abdominal aorta. From this dataset the
portion of the aorta including the aortic arch and the thoracic aorta was considered
for a simulation in a moving domain. The aorta was then segmented with VMTK at
all the 10 time frames available, and the tracking procedure was applied to extract
the 10 displacement fields describing the vessel wall motion over the cardiac cycle.
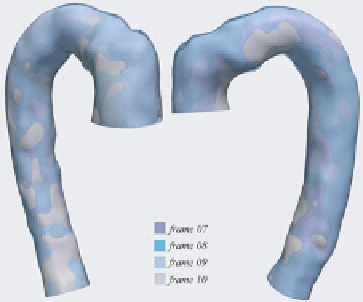
Fig. 12.6 represents some of the reconstructed surfaces at different time frames: they
are simply superimposed prior to the registration procedure in order to highlight the
misalignment due to their movement. Fig. 12.7 depicts the results of the registration
procedure (performed with an
ad hoc
Matlab code) for two consecutive surfaces. In
the rightmost panel frame 1 has been mapped to frame 2.
Fig. 12.6.
Synopsis of the last 4 frames superimposed before tracking has been performed
Fig. 12.7.
Detail of two frames of the aorta before and after the registration