Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
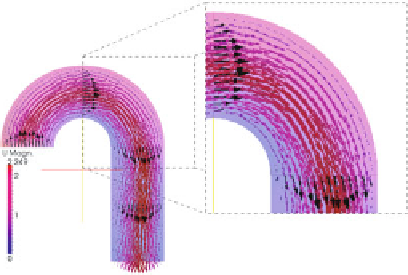
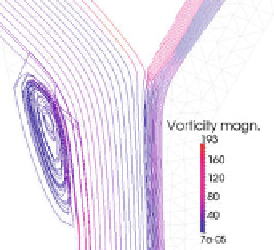
Fig. 12.5.
Left: DA assimilation on 2D a curved domain. Black arrows are the data to be assim-
ilated. The red arrows (colores refer to the pressure) are the results after the DA procedure. The
results of DA are closer to the reference solution, highlighting the role of DA as a filtering proce-
dure for the noise of the data. Right: vorticity in a 2D bifurcation computed by the DA procedure
solution on the fine mesh. It is evident that the DA leads to a more accurate estimate
of the WSS, the improvement being more evident as the SNR gets smaller.
12.2.3 Perspectives
Assimilation of (velocity) data into the simulation of an incompressible fluid is a
problem whose interest goes beyond the specific medical applications, and different
methods are viable. In [34] Least Squares Finite Elements are used because of their
versatility in managing different boundary conditions. In [41], merging of velocity
data is carried out by using a “virtual” forcing term as CV. Here, we resorted to a
control approach that in preliminary test cases provides promising results. Sufficient
conditions for the well posedness of the linearized Oseen problem are given. Many
challenges are however open by these preliminary results. Beyond (and before) an
extensive use of DA in clinical practice, there are at least two main concerns that
deserve an accurate consideration.
Analysis of the impact of the noise.
An extensive analysis of this aspect is in order
to identify the reliability of the results. Modelling the impact of uncertainty on the so-
lution of partial differential equations is an up-to-date topic (see e.g. [59, 60] and the
recent work [61], comparing Galerkin vs collocation methods). Different approaches
can be pursued and different sources of noise should be considered, depending on
the measurement devices (see e.g. [62] and Chapter 3 of [20]). A
sensitivity analysis
of quantities of interest such as the WSS on the noise affecting the data would clar-
ify the robustness of the procedure to the perturbations. More advanced approaches
are based on the moment method, the Bayesan approach, the polynomial chaos (see
e.g. [27]). Extensive investigations on this aspects, with different approaches, will
be carried out as a follow up of the present results.