Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
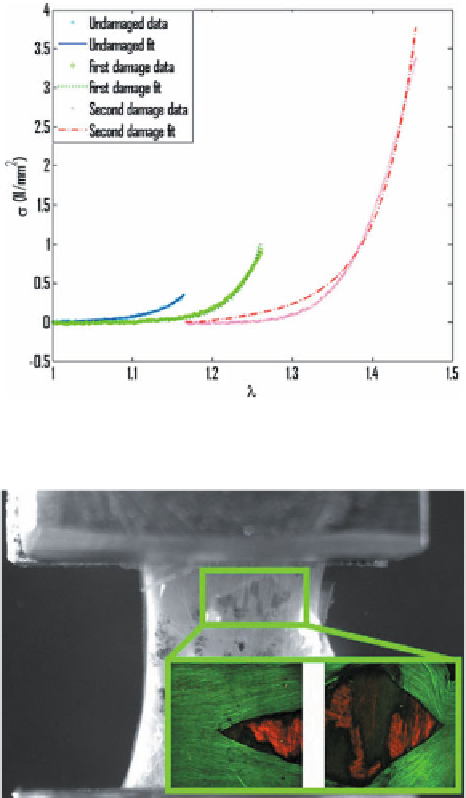
Fig. 6.11.
Damage results for a strip of basilar artery tissue loaded in the circumferential direction.
Data were fit to the discontinuous acute rupture model
Fig. 6.12.
Damage from circumferential testing is evident on the macroscale towards the upper
region of the tissue, shown here clamped at a stretch of approximately 1.45. Inset: Multi-photon
image from MetaMorph depicting the damage shown in the left image. The elastin (green) appears
torn and pulled away from the underlying medial collagen (red), bar = 50
μ
m
circumferentially oriented collagen in the media (Fig. 6.12). Values for material
parameters were:
λ
a
=
1
.
16
±
0
.
08,
η
iso
=
69
.
0
±
85
.
9kPa,
γ
iso
=
17
.
8
±
14
.
5,
=
±
=
.
±
.
η
677
615 kPa,
γ
5
6
2
4. Values for damage parameters were
aniso
aniso
=
.
±
.
=
.
±
.
=
.
±
.
λ
1
31
0
08,
c
1
2
9
1
5,
α
28
9
33
5. Note that
λ
s
, the stretch at
s
1
f
1
s
in Eq. (6.52).
R
2
the start of elastin damage, was used to compute
α
values were
typically close to unity for each specimen.
The damage observed in these experiments is on a scale larger than what can
be reasonably considered in continuum damage mechanics. The continuum damage