Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
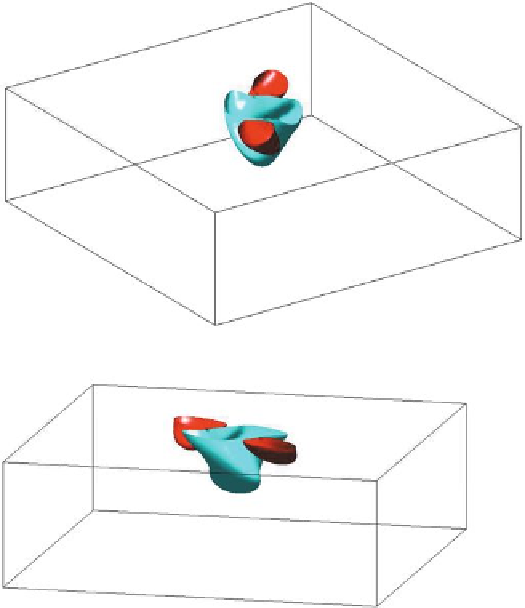
Fig. 5.4.
Slab with transmural fibre rotation. Anodal stimulation applied to a slab with unequal
anisotropy ratio. Two different views of the isopotential surfaces of the transmembrane potential
distribution of values
−
88 and
−
75 mV, 2 ms after the beginning of the stimulation
regions but only an slightly twisted elliptical hyperpolarized region centered at the
stimulation site; see Fig. 5.3, bottom left panel. This confirms that
virtual electrodes
can only be generated by bidomain models with unequal anisotropy ratios of the
intra- and extracellular media. The formation of the two virtual cathodes elicited
by the anodal stimulation explains why an anodal stimulation is able to excite the
myocardium, as shown by the excitation sequence shown in Fig. 5.5 and described
below.
Excitation wavefront sequence elicited by anode make mechanism.
The iso-
chrones of activation time on the epicardial surface and transmural diagonal sections
displayed in Fig. 5.5 show clearly that the first-triggered areas are the two epicardial
sites located at the center of the virtual cathodes, generating two distinct excitation
wavefronts propagating outward and inward along the diagonal parallel to the fibre
direction. When the excitation isochrones reach points lying on a boundary of the
virtual anode, a block of the inward propagation takes place since this region is inex-
citable until the stimulus is turned off. Therefore, from about 2 to 6 ms, two distinct
activation wavefronts propagate outwards on the epicadial surface, moving faster